Introduction to Drosophila
Introduction to Drosophila
Other infor you can read: socmucimm, 2014
This notes from the Youtube video: Walter Jahn; GENETICS: Drosophila; 2020
Usual
USA/Upstream Activating Sequences
Videos: Lecture 5 Drosophila; UVUProfessor; 2015/02/09
Text Lecture: DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 3230; utah.edu
Why Drosophila
- Ideal for genetic studies
- Rapid life cycle
- Readiness to bread
- Polytene chromosomes
- Phenotypic mutatans
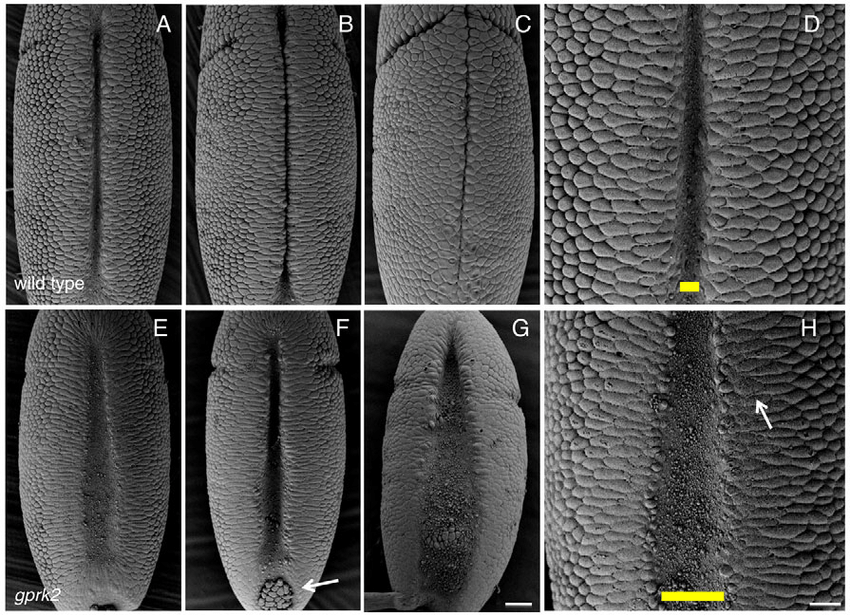
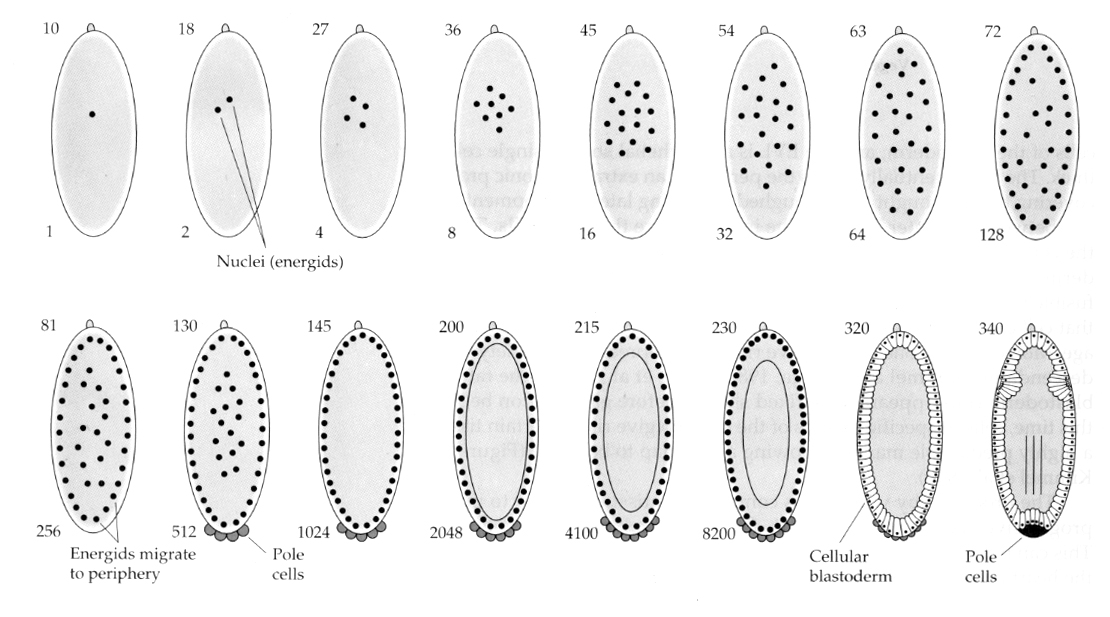
- Superficial Cleavage
- Pull the egg surface down and to form cell membrane
- Centrally located yolk confines cleavage to the cytoplasmic rim of the egg
- Syncytial blastoderm
- All cleavage nuclei are contained within a common cytoplasm
- Cellular blastoderm
- Each somatic nucleus is partitioned into a single cell
Gastrulation
Reading Materials:
- Mid-blastula transition
- Gastrulation begins
- Slowdown of nuclear division
- Increase in RNA transcription
- Ventral furrow
- Invagination of prospective mesoderm
- Cephalic furrow
- Separates procephalon from the germ band
- Germ band
- Convergent extension
Anterior-Posterior Polarity
- Maternal effect genes
- Gap genes
- Pair-rule genes
- Segment polarity genes
- Homeotic selector genes
Development
- Oocyte develops and inside the ovary surrounded by support cells
- Nurse and follicle cells deposit maternal effect mRNA and proteins, and send signal essential for development to the Oocyte.
- After fertilization, the embryo establishes distinct regions based on expression patterns of maternal and zygotic genes.
- Segmentation and differentiation of the embryo corresponds to adult structures.
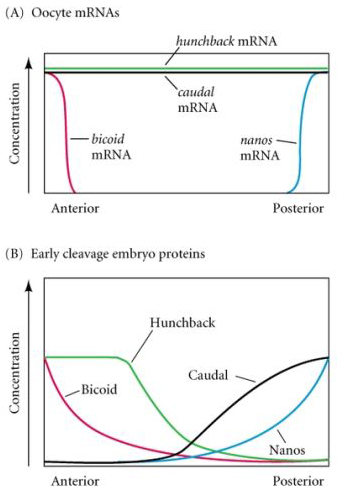
Maternal effect genes
 |
 |
 |
|---|
- bicoid and Hunchback
- Define anterior organizing center
- Nanos and Caudal
- Define posterior organizing center
- Torso
- Define terminal boundary region
A-P Pattern
Gene Expression patterns
Gap gene expression pattern
Inhibit each other by followed the hierarchy of them
 |
|---|
- Pair-rule gene: fushi tarazu
- Segment Polarity genes: engrailed and wingless
- Segments and Parasegements
- Homeotic (Bub) Genes
Introduction to Drosophila