NextDenovo: an efficient error correction and accurate assembly tool for noisy long reads
- Quick Start
- Tutorial
- Other related Long reads Assembly Tools, check the end of the post, for example: Falcon (Chin et al. 2016), Canu (Koren et al. 2017), WTDBG2 (Ruan and Li 2020), or Flye (Kolmogorov et al. 2019)
NextDenovo
Background
- Third-generation long-read:
PacBio has high-fidelity (HiFi) reads but they are relatively short (~ 15 kb). So, it is unable to span long tandem or highly homologous multi-copy repeats like centromeres. ONT sequencing can generate > 100-kb “ultra-long” reads. - CTA and ATC:
“correction then assembly” (CTA, an assembler first corrects errors in the reads and then uses the corrected reads for assembly) and “assembly then correction” (ATC, an assembler uses error-prone reads to assemble the genome and then corrects errors in the assembled genome) are commonly used in assembly. CTA is much slower. But in terms of the assembly of segmental duplications/repeats, and especially for large plant genome assemblies, the CTA-based strategy usually has an enhanced ability to distinguish different gene copies and produce more accurate and continuous assemblies. NextDenovo is the tool of CTA-based assembly tool
Steps
-
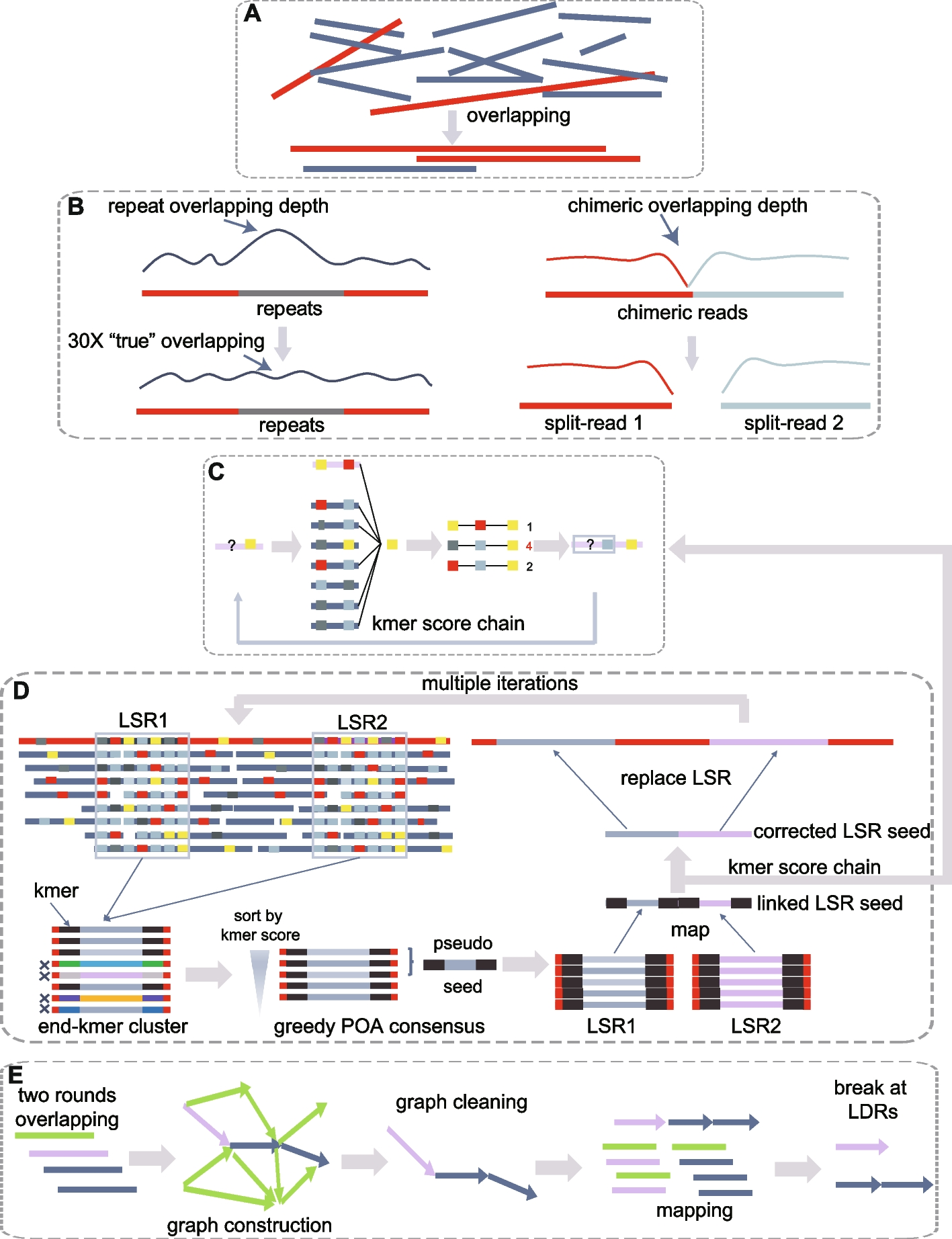
Detecting Overlapping Reads
- Initial Detection: Detects overlapping reads (Fig. 1A).
- Filtering: Filters out alignments caused by repeats.
- Splitting: Splits chimeric seeds based on overlapping depth (Fig. 1B).
-
Rough Correction with KSC Algorithm
- Algorithm Used: Kmer score chain (KSC) algorithm, used in NextPolish [19], for initial rough correction (Fig. 1C).
-
Handling Repeated Regions
- Detection of Low-Score Regions (LSRs): Uses a heuristic algorithm during traceback within the KSC algorithm.
- Accurate Correction:
- Combines partial order alignment (POA) [20] and KSC.
- Collects subsections spanning LSRs and generates kmer sets at flanking sequences.
- Filters subsections with lower kmer scores.
- Creates pseudo-LSR seeds from top-ranked subsections using a greedy POA consensus algorithm.
- Maps and corrects pseudo-LSR seeds multiple times for accuracy.
- Integrates corrected LSRs back into the primary corrected seed (Fig. 1D).
-
Pairwise Overlapping and Dovetail Alignments
- Two Rounds of Overlapping:
- First Round: Uses rapid detection parameters.
- Second Round: Applies rigorous parameters for accurate alignments.
- Graph Construction:
- Constructs a directed string graph.
- Removes transitive edges using the “best overlap graph” (BOG) algorithm.
- For repeat nodes, edges are only removed if below specific thresholds to maintain connectivity.
- Removes tips and resolves bubbles.
- Two Rounds of Overlapping:
-
Progressive Graph Cleaning
- Simplifying Subgraphs:
- Uses a progressive cleaning strategy with increasingly stringent thresholds.
- Breaks paths at nodes with multiple connections.
- Outputs contigs from broken linear paths.
- Reducing Misassemblies:
- Maps all seeds to contigs.
- Breaks contigs at lower mapping depth regions (LDRs) (Fig. 1E).
- Simplifying Subgraphs:
Key Algorithms and Techniques
- KSC Algorithm: Used for initial rough correction and handling LSRs.
- Heuristic and Accurate Algorithms: For detecting and correcting LSRs.
- BOG Algorithm: For removing transitive edges in the graph.
Error Correction
NextDenovo is 1.63 times faster on real data compared to Consent, Canu, and Necat. As the read length increases, the time required for correction also increases. However, NextDenovo and Necat demonstrated only slight increases, while Canu exhibited a significant increase in processing time
Installation
|
Run
|
Example of run.cfg
[General] job_type = local job_prefix = nextDenovo task = all rewrite = yes deltmp = yes parallel_jobs = 22 input_type = raw read_type = ont # clr, ont, hifi input_fofn = input.fofn input_fofn2 = input2.fofn workdir = HG002_NA24385_son_assemble [correct_option] read_cutoff = 1k genome_size = 3g # estimated genome size sort_options = -m 50g -t 30 minimap2_options_raw = -t 8 pa_correction = 5 correction_options = -p 30 [assemble_option] minimap2_options_cns = -t 8 nextgraph_options = -a 1
Result
- Sequence:
01_rundir/03.ctg_graph/nd.asm.fasta - Statistics:
01_rundir/03.ctg_graph/nd.asm.fasta.stat
Assembly data: 109G+98G
RAM utility: about 400GB. (You can also make it run with 64 RAM but it would takes much loger time to finish)
Time: about 2 days.
After Assembly
Compare the result from the SKLA1.0 by MUMmer
|

According to this result, the first three chromosomes from bottom to top are chr1, chr2, and chr3. The x-axis, from left to right, is sorted by the length of the contigs. As we can see, the first contig represents the full length of chr3. Contigs 2, 3, and 7 represent chr1, while contigs 6, 8, and 9 are three pieces of chr2. Another very interesting result is that, except for chr2, both chr1 and chr3 are complemented and reversed.
NextPolish
NextPolish was also recomand. You can download and install by following the instruction form github. But I am not that luck to install it in my Ubuntu server. It come with the error:
gcc -g -Wall -Wno-unused-function -O2 -DHAVE_PTHREAD -DUSE_MALLOC_WRAPPERS bwashm.o bwase.o bwaseqio.o bwtgap.o bwtaln.o bamlite.o bwape.o kopen.o pemerge.o maxk.o bwtsw2_core.o bwtsw2_main.o bwtsw2_aux.o bwt_lite.o bwtsw2_chain.o fastmap.o bwtsw2_pair.o main.o -o bwa -L. -lbwa -lm -lz -lpthread -lrt /usr/bin/ld: ./libbwa.a(rope.o):/raid/home/wenkanl2/BioTools/NextPolish/util/bwa/rle.h:33: multiple definition of `rle_auxtab'; ./libbwa.a(bwtindex.o):/raid/home/wenkanl2/BioTools/NextPolish/util/bwa/rle.h:33: first defined here /usr/bin/ld: ./libbwa.a(rle.o):/raid/home/wenkanl2/BioTools/NextPolish/util/bwa/rle.h:33: multiple definition of `rle_auxtab'; ./libbwa.a(bwtindex.o):/raid/home/wenkanl2/BioTools/NextPolish/util/bwa/rle.h:33: first defined here collect2: error: ld returned 1 exit status make[2]: *** [Makefile:30: bwa] Error 1 make[2]: Leaving directory '/raid/home/wenkanl2/BioTools/NextPolish/util/bwa' make[1]: *** [Makefile:19: bwa_] Error 2 make[1]: Leaving directory '/raid/home/wenkanl2/BioTools/NextPolish/util' make: *** [Makefile:18: all] Error 2
So, I tied install it with bioconda:
|
nextpolish-1.4.1 | py311h99925d8_3 1.7 MB bioconda
And them, it installed the version 1.4.1. Next, I tried the test: nextPolish test_data/run.cfg and it finished the test correctly:
Type Length (bp) Count (#) N10 60501 1 N20 60501 1 N30 60501 1 N40 60501 1 N50 60501 1 N60 51048 2 N70 51048 2 N80 51048 2 N90 51048 2 Min. 51048 - Max. 60501 - Ave. 55774 - Total 111549 2
Options for NextPolish
[sgs_option]: Polishing using short reads only
[lgs_option]: Polishing using long reads only
In Action:
|
cfg file for this experiment:
[General]
job_type = local
job_prefix = nextPolish
task = default
rewrite = yes
rerun = 3
parallel_jobs = 20
multithread_jobs = 20
genome = result/NextDenovo_result.fa
genome_size = auto
workdir = ./01_rundir
polish_options = -p {multithread_jobs}
[sgs_option]
sgs_fofn = ./sgs.fofn
sgs_options = -max_depth 100
In this config file, it given the number of parallel jobs as 20 and multithread jobs as 20, which means the max threads allocated would be 20*20 = 400. So,be sure about that you have that much of threads for calculation or it would make the whole processes slower than normal.
Other Long-Reads Assembly Tools
LongStitch: Enhancing Genome Assembly with Long Reads
LongStitch[1] is a powerful computational tool designed to improve the quality of genome assemblies by utilizing long-read sequencing data. It addresses common issues in genome assembly, such as errors and gaps, that are often introduced during the assembly of short-read sequences.
It was published at 2021. Until the July 2024, it got 34 citations. It is an open source software and deposit in GitHub with 42 starts.
Key features of LongStitch include:
- Error Correction: By aligning long reads to the existing genome assembly, LongStitch identifies and corrects misassemblies, leading to a more accurate genomic representation.
- Scaffolding: LongStitch leverages long reads to link contigs into scaffolds, significantly enhancing the continuity and completeness of the genome assembly.
- High-Quality Output: The resulting assemblies are more comprehensive and accurate, making them invaluable for further genomic analysis and research.
LongStitch’s ability to handle repetitive regions and complex genomic structures makes it an essential tool for researchers aiming to achieve high-quality genome assemblies.
Coombe L, Li J X, Lo T, et al. LongStitch: high-quality genome assembly correction and scaffolding using long reads[J]. BMC bioinformatics, 2021, 22: 1-13. ↩︎
NextDenovo: an efficient error correction and accurate assembly tool for noisy long reads