ATAC-seq: A Powerful Tool for Mapping Gene Regulation
Introduction:
The regulation of gene expression is a complex process that involves the interplay of various factors, including transcription factors, enhancers, promoters, and silencers. Understanding the dynamics of gene regulation is essential for unraveling the mysteries of cellular development, differentiation, and disease progression. To address this challenge, researchers have developed a powerful tool called ATAC-seq, which enables the mapping of gene regulation at an unprecedented scale and resolution. In this blog, we will delve into the world of ATAC-seq and explore its applications, advantages, and limitations.
What is ATAC-seq?
ATAC-seq (Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin sequencing) is a genomic technique that allows researchers to profile the open chromatin regions in a given cell type. Open chromatin regions are those that are accessible to a transposase enzyme, which is used to fragment the chromatin into smaller pieces. The resulting fragments are then sequenced, producing a map of open chromatin regions across the genome.

Principle:
The principle behind ATAC-seq is straightforward. The assay involves the following steps:
- Crosslinking: Cells are fixed with formaldehyde to create covalent bonds between proteins and DNA.
- Shearing: Chromatin is sheared into smaller fragments using a transposase enzyme.
- End repair and A-tailing: The 3’ ends of the fragmented DNA are repaired and modified to generate blunt ends.
- Sequencing library preparation: The modified DNA fragments are then prepared for sequencing using standard library preparation protocols.
- Sequencing: The sequencing step generates millions of reads that are then mapped back to the reference genome.
Advantages:
- High resolution: ATAC-seq offers high resolution mapping of open chromatin regions, allowing researchers to identify regulatory elements at a genomic scale.
- Sensitivity: The technique is highly sensitive, capable of detecting rare regulatory elements that would be missed by other methods.
- Cost-effective: ATAC-seq is relatively cost-effective compared to other techniques such as ChIP-seq, which requires expensive antibodies and specialized equipment.
- Genome-wide analysis: ATAC-seq allows for genome-wide analysis of open chromatin regions, enabling researchers to identify patterns and trends in gene regulation.
- Identification of novel regulatory elements: ATAC-seq can identify novel regulatory elements that were previously unknown or unannotated, providing new insights into gene regulation.
- Investigation of gene regulation in specific cell types or tissues: ATAC-seq can be used to study gene regulation in specific cell types or tissues, providing valuable insights into cellular differentiation and development.
- Identification of disease-associated regulatory elements: ATAC-seq can be used to identify regulatory elements that are associated with diseases, providing new targets for therapeutic intervention.
- Monitoring of gene regulation changes over time: ATAC-seq can be used to monitor changes in gene regulation over time, providing insights into how gene regulation dynamics contribute to cellular processes.
Limitations:
- Limited to accessible chromatin regions: ATAC-seq only maps open chromatin regions that are accessible to the transposase enzyme, which means that closed chromatin regions remain unmapped.
- Biases in sequencing libraries: Sequencing libraries can introduce biases in the form of overrepresented or underrepresented regions, which can impact downstream analyses.
- Interpretation challenges: Interpreting ATAC-seq data requires advanced computational skills and knowledge of bioinformatics tools and methods.
- Limited spatial resolution: ATAC-seq provides a snapshot of open chromatin regions at a particular time point, but does not provide information on the spatial organization of regulatory elements.
Applications:
- Stem cell biology: ATAC-seq has been used to study the gene regulation landscape in stem cells, providing insights into pluripotency and lineage commitment.
- Cancer research: ATAC-seq has been applied to cancer research, identifying regulatory elements that are associated with tumor progression and metastasis.
- Developmental biology: ATAC-seq has been used to study the gene regulation landscape in the brain, providing insights into neural development, synaptic plasticity, and neurological disorders.
- Immunology: ATAC-seq has been applied to the study of immune cells, revealing regulatory elements that control immune cell function and differentiation.
- Plant biology: ATAC-seq has been used to study gene regulation in plants, providing insights into plant development, stress response, and photosynthesis.
- Microbiology: ATAC-seq has been used to study gene regulation in microbes, including bacteria and yeast, providing insights into the regulation of virulence factors and drug resistance.
- Drug discovery: ATAC-seq can be used to identify potential drug targets by analyzing the regulatory elements that control gene expression in diseased cells.
- Personalized medicine: ATAC-seq can be used to study gene regulation in individual patients, providing insights into personalized therapies and treatment strategies.
- Synthetic biology: ATAC-seq can be used to design and engineer gene circuits for synthetic biology applications, such as biofuels, drugs, and other valuable compounds.
Summary
In summary, ATAC-seq is a powerful tool for studying gene regulation and has a wide range of applications in various fields, from basic research to drug discovery and personalized medicine.
Pipelines for ATAC-Seq
- Encodeproject: ATAC-seq Data Standards and Processing Pipeline
- ENCODE-DCC/atac-seq-pipeline
- Yiwei niu; 2019: ATAC-seq data analysis: from FASTQ to peaks
- John M. Gaspar; 2019; ATAC-seq Guidelines
- Lucille Delisle; 2023; ATAC-Seq data analysis
Data Analysis Pipeline
According to Fen Yan[1]
- pre-analysis: quality check and alignment
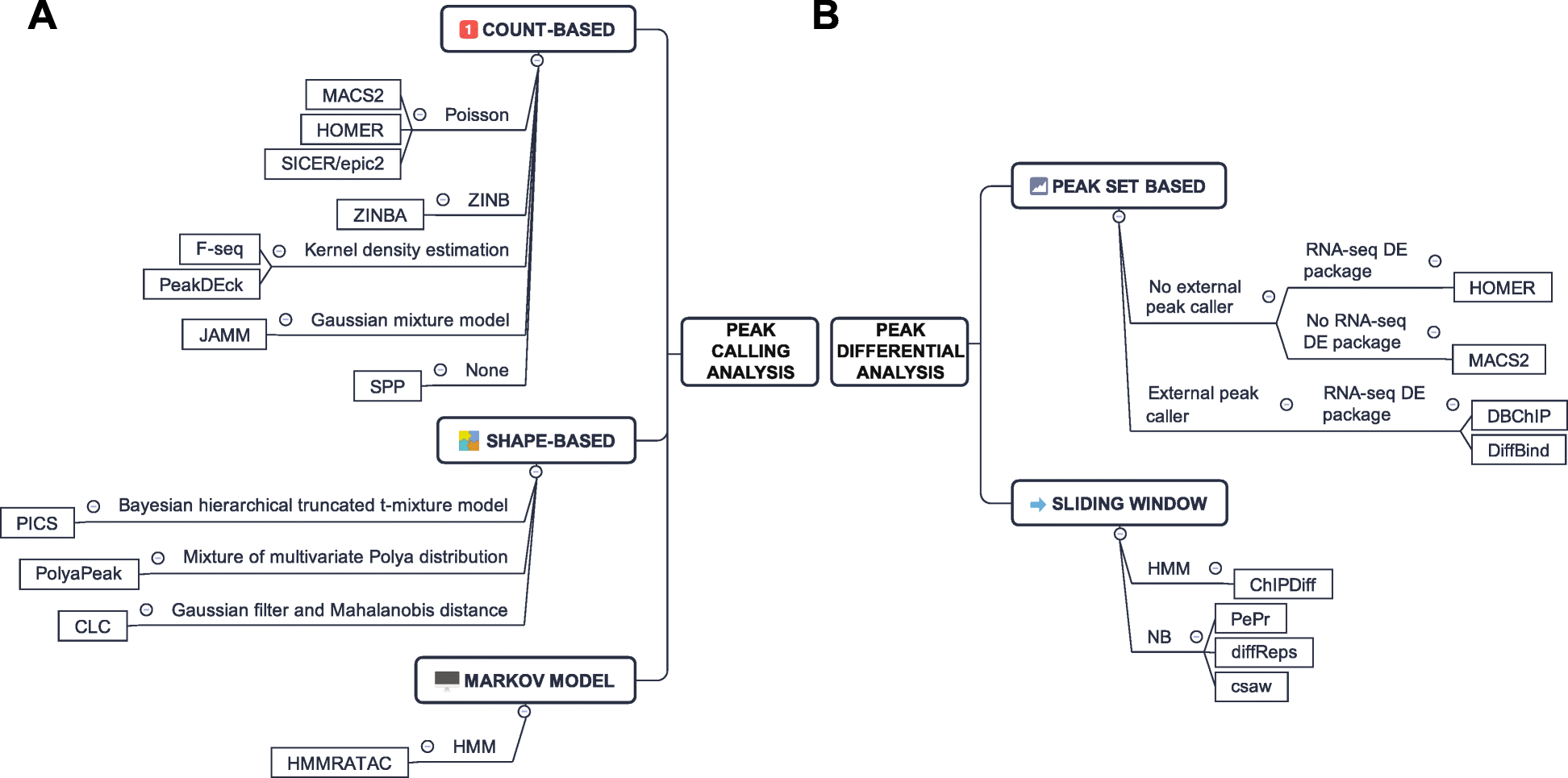
- core analysis: peak calling
- advanced analysis:
- peak differential analysis and annotation
- no differential peak analysis tools have been specifically developed
- motif enrichment
- footprinting
- nucleosome position analysis
- peak differential analysis and annotation
 |
|---|
| Fen Yan |
Yan, F., Powell, D.R., Curtis, D.J. et al. From reads to insight: a hitchhiker’s guide to ATAC-seq data analysis. Genome Biol 21, 22 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-020-1929-3 ↩︎
ATAC-seq: A Powerful Tool for Mapping Gene Regulation








