Super Conductor
Super Conductor
Source: The Stuff of Dreams, Scientific American; Oct 2019
Could new theoretical and computational advances finally deliver the elusive room-temperature superconductor?
BCS theory
(Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer theory)
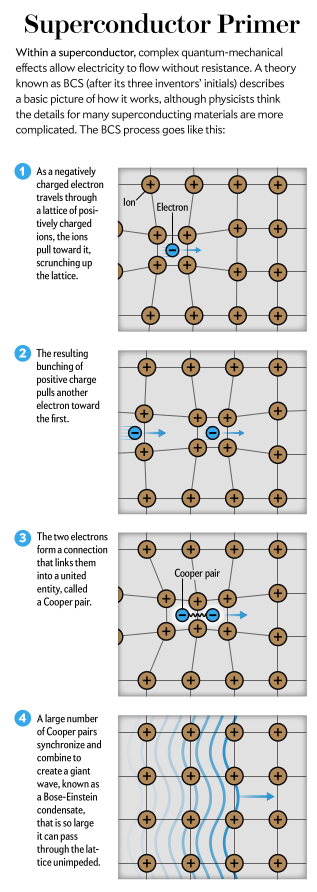
| The properties of Type I superconductors were modeled successfully by the efforts of John Bardeen, Leon Cooper, and Robert Schrieffer in what is commonly called the BCS theory. A key conceptual element in this theory is the pairing of electrons close to the Fermi level into Cooper pairs through interaction with the crystal lattice. This pairing results from a slight attraction between the electrons related to lattice vibrations; the coupling to the lattice is called a phonon interaction. – R Nav 1. Electron moves through the lattice will pull the atoms in lattice, and bunches positives charges together as a result. 1. The positive charges will pull another electron into the first wake, Cooper pair formed between the two particulars. 1. Those pairs behavior like waves name as Bose-Einstein condensate that is too large to be impeded by the lattice and so flows through it without any resistance at all. |
 |
|---|---|
| ©2019 Scientific American AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA |
Machine learning in super conductor
2018, one algorithm trained on a database of thousands of materials, developed ability to identify superconductors in another data set with 92 percent accuracy and to estimate their critical temperatures.
It did so using only simple elemental properties such as atomic weight and melting temperature.
Shortcoming: There is something you do which works, and you just keep doing exactly the same thing to make it work, and why you do it you have no idea. --Somayazulu
Extra Reading
Superconducting Transistor
 |
|---|
| © news.mit.edu |
Transistor:
“Transistor, semiconductor device for amplifying, controlling, and generating electrical signals. Transistors are the active components of integrated circuits, or “microchips,” which often contain billions of these minuscule devices etched into their shiny surfaces. Deeply embedded in almost everything electronic, transistors have become the nerve cells of the Information Age.”-- Michael Riordan[1]
Applying[2]:
- Highly sensitive situation: Monitory brain activity
- quantum and classical computing.
Josephson junction:
- Traditional superconducting transistor is a device invented in the 1960s.
- Essentially two superconductors separated by a thin insulator.
Shortcoming of the traditional superconducting transistor:
- finicky
- expensive
- prone to err
- low temperature working environment
Cryotron
- Developed by Dudley Buck, MIT electrical engineer, in 1956.
- The device was little more than two superconducting wires: One was straight, and the other was coiled around it.
- Much smaller than current computing switches like vaccum tubes.
- 1959, Buck died in suddenlu at age 32. The program was ceased.
Superconducting Nanowire
To overcome the disadvantages of Josephson junction, Karl Berggren’s group developed the nanowire, whcih is based on the Cryotron.
- Switch is triggered by magnetic, rather than heat.
The infromation of this block was mainly form Science Daily[2:1]
Michael Riordan
Professor of Physics, Institute for Particle Physics, University of California at Santa Cruz, and Professor of History and Philosophy of Science, Stanford University, Stanford, Calif. Author of Crystal…link ↩︎Daniel Ackerman
MIT News Office, Nanowire could provide a stable, easy-to-make superconducting transistor, Feb 11, 2021. ScienceDaily. link ↩︎ ↩︎








