Modifications of digestive enzymes in trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and sea bream
Modifications of digestive enzymes in trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and sea bream
(Sparus aurata) in response to dietary fish meal replacement by plant protein sources
Cite: Santigosa E, Sanchez J E, Medale F, et al. Modifications of digestive enzymes in trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and sea bream (Sparus aurata) in response to dietary fish meal replacement by plant protein sources[J]. Aquaculture, 2008, 282(1): 68-74.
General Information
trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)

img from: nyfalls.com, Copyright belongs to the author
Abstract
- Three experimental diet (50%, 75%, 100%)
- Rainbow trout and gilthead sea bream
- Compare the digestion enzymes
- Post-prandial protease and α-amylase activities
- protease Activities change
- chymotrypsin-like bands
- α-amylase activities does not affected
- histology Change
- intestinal length
- Weight change only on PP100
Introduction
###P1: Plant protein substitution for economy
Shortcomings:
- hgih carbohydrate levels
- isoflavones
- low methionine levels
- anti-nutritional factors
They can:
- impede protein digestion
- impair immune responses
- intestinal inflammation.
End: Yellow perch is one of the most sensitive species for this change.
P2: Pancreas
- Serine-protease (trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase and collagenase)
- Glucosidases
- hydrolyze starch into lineal chains
P3: Our purpose
- Protine and Carbohydrate digestion
- histology
M&M
- Chemicals
- Diets, animals and growth experiment
- Post-parndial experiment and sampling
- Preparation of extracts and determination of soluble protein
- Enzyme assays
- Zymograms: characterization of protease fractions and inhibition by PP diets
- Proximal intestine histological analysis
- Statistical analysis
Results
Enzymes activities
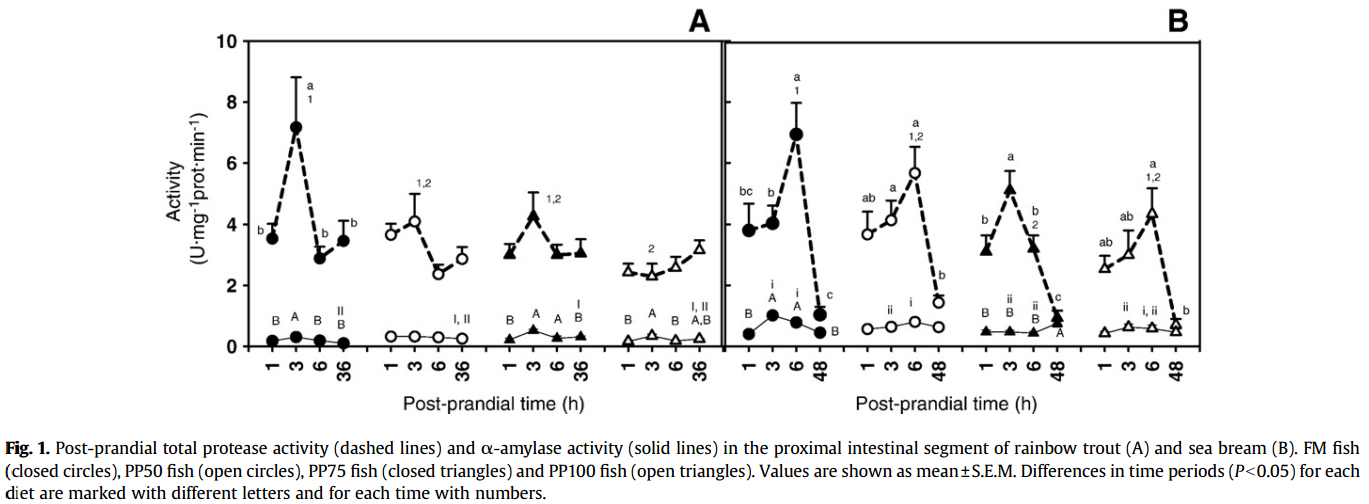
Alkaline Protease
- Trout fed diets PP50 and PP75 showed only a slight post-feeding increase in this activity.
- Sea bream fed the FM diet showed a maximum of 6.93±1.03 U protease·mg− 1 protein·min− 1. This value decreased gradually as the percentage of plant protein increased
Amylase
a significant post-prandial increase in this activity was recorded only in PP75 and PP100 fed trout. Replacement of fish meal by plant protein did not induce significant changes in α-amylase activity in either species.
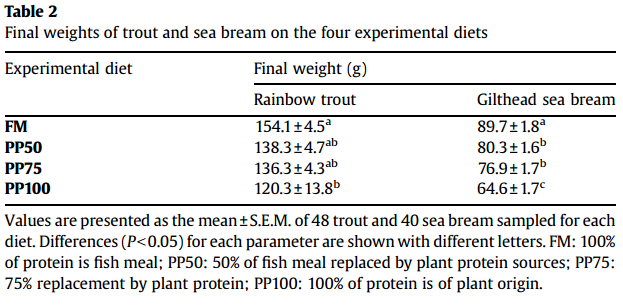
Growth Performance
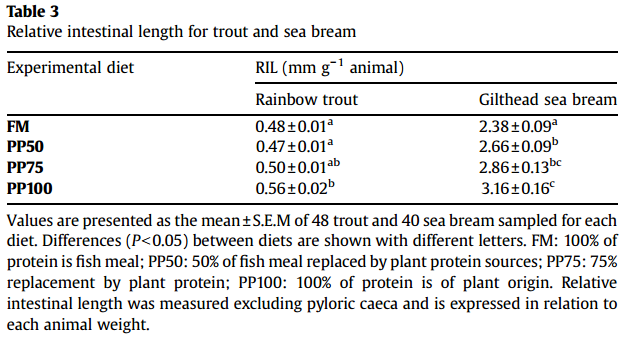
Intestine Growth
Related Notes:
Modifications of digestive enzymes in trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and sea bream
https://karobben.github.io/2020/08/12/LearnNotes/Paper_Diet_Switch_Fish4/








