Principles of Biochemistry 22 |Nucleic acids| Class Notes |HarvardX
Quick review
- Building blocks of nucleic acids
- Energy currency in cells (ATP)
- Precursors of universal electron acceptors
- Signaling molecules
RAN: Ribose; DNA: Deoxyribose
Purines: A (Adenine), G (Guanine)
pyrimidine: T (Thymine), C (Cytosine), U (Uracil)
Nucleosides:
- pentos + purine/pyrimidine
- nucleic acid without a phosphate group
e.g. Adenosine
Nucleotides:
- petos + purine/pyrimidine + one or more phosphates
- Nucleic acid with three phosphates group
e.g. ATP
DNA/RNA:
- polymerized Nucleotides are linked by a phosphodiester linkage
- Ribonucleotide: RNA
- Dexoyribonucleotide: DNA
Nucleotides Biosynthesis
PRPP: phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate
PRPP + base $\to$ NMP + PPi
novo pathway:
PRPP + amino acids + HCO3- + folate + … $\to$ nucleotide
Glucose-6-P $\overset{Pentose\ phosphate\ pathway}{\to}$ Ribose-5-P $\to$ PRPP
Another contribution of nucleotides
Coenzyme A; cAMP
Novo nucleotide biosynthesis

Inositol monophosphate (IMP) $\to$ AMP/GMP
PRPP $\to$ IMP has 11 steps
-
carbonyl activation
$Glycine + ATP \to Glycine-P + ADP $
The carbonyl oxygen of glycine is activated by phosphorylation. -
Displacement by amine
$Glycine-P + NH_ 2 -R \to Glycine-NH-R$ R is nucleotide
…
Purine Biosynthesis:
- By Biochemistry Den (Recommended)
- By Hidaya Aliouche, B.Sc.
- by Sagar Aryal
IMP to AMP/GMP
Regulation of the synthesis
Biosynthesis of pyrimidine
$UMP \to UTP \to CTP$
Formation of the pyrimidine-ring:
- $Carbamoyl-P + Aspartate \overset{ATCase}{\longrightarrow} Carbamoyl aspartate$
- $Carbamoyl aspartate \overset{Dihydroorotase}{\longrightarrow} Dihydroorotate$
- $Dihydroorotate + NAD^ +\overset{Dihydroorotate\ Dihydroorotase}{\longrightarrow} Orotate + NADH + H^ +$
Pyrimidine assemble
- $Orotate + PRPP \to UMP + PP_ i + CO_ 2$
- $UMP + 2ATP \to UTP + 2ADP$
- $UTP + ATP + Gln \to CTP + ADP + P_ i + Glu$
NDP to dNDP
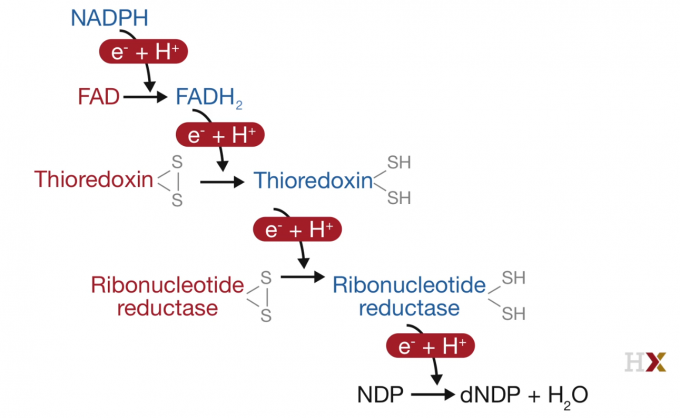
Cancer Treatment
The cancer cell is more sensitive than normal cells to inhibitors of nucleotide biosynthesis
- $dUMP \overset{Thymidylate\ synthase}{\longrightarrow} dTMP$
Folate cycle
Catabolism
Pyrimidine catabolism
$Uridine + Pi \underset{phophorylase}{\overset{Pyrimidine-}{\longleftrightarrow}} Ribose-1-phosphate + Uracil$
$Uracil + NADPH \to Dihydrouracil + NADP^ +$
$Dihydrouracil \overset{Ring cleavage}{\longrightarrow} \beta-alanine + CO_ 2 + NH_ 4^ +$
Adenosine degradation
$Adenosine \ monophosphate (AMP) + H_ 2O \to P_ i + Adenosine$
$Adenosine + H_ 2O \to Inosine + NH_ 3$
$Inosine + H_ 2O \to Ribose + Hypoxanthine$
$Hypoxanthine + O_ 2 + H_ 2O \to Xanthine+ H_ 2O_ 2$
Guanosine degradation
$GMP + P_ i \to Guanosine + H_ 2O$
$Guanosine + H_ 2O \to Ribose + Guanine$
$Guanine + H_ 2O \to Xanthine + NH_ 3$
$Xanthine \overset{Xanthine \ oxidase}{\longrightarrow} Uric \ acid$
Accumulation of Uric acid in blood could cause gout.
treatment
- Reduce the formation of uric acid
Hypoxanthine and Allopurinal could serve as potent xanthine oxidase inhibitors. By restricted the production of the uric acid, the xanthine remained. But it is more soluble and easy to be cleaned. - Uric acid degradation
$Uric acid \overset{Urate oxidase}{\longrightarrow} Allantoin$
Pyrimidine/Purine salvage
Pyrimidine
$Uracil \longleftrightarrow Ribose-1-P$
$Ribose-1-P \overset{Pyrimidine \ phosphorylase}{\longleftrightarrow} Uridine + P_ i$
Purine
$Adenine + PRPP \overset{APRT}{\longrightarrow} Adenosine \ monophosphate$
APRT: adenine phosphoribosyltransferase.
$Guanine + PRPP \overset{HPRT}{\longrightarrow} Guanine \ monophosphate$
HPRT: hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase.
Lesch-Nyhan disease
Genetic deficiency in HPRT
X-linked (Uncommon in females)
It causes Hyperuricemia, Severn neurological symptoms
Allopurinol treats hyperuricemia, but no neurological symptoms.
Principles of Biochemistry 22 |Nucleic acids| Class Notes |HarvardX
https://karobben.github.io/2021/06/18/LearnNotes/edx-biochm-22/









