Principles of Biochemistry 23 |Carbohydrate metabolism| Class Notes |HarvardX
Transporters
Glucose is not permeable to the cell membranes. So, the transporter is needed for cells absorbing glucose.
Quick View: Glucose Transporters (GUL1)
- Passive transport: Glucose moves with the concentration gradient
- Not a channel: Transport is slower than diffusion
Model of GUL1: Stepwise transfer
Monosaccharide import
Glucose, galactose, fructose use GLUT transporters.
RBCs: glucose and galactose but not fructose transported by GLUT1
Liver: GLUT2 transports glucose, galactose, and fructose
Glycolysis of monosaccharide
galactose
This net gain of 2 ATP per galactose from glycolysis
fructose
In glycolysis, hexokinase has a much higher affinity for glucose than for glucose. As a consequence, it phosphorylates the fructose only when the concentration of glucose is low. e.g.: adipocytes
$$
Fructose +ATP \overset{Fructokinase}{\longrightarrow} Fructose^ {_ -}1^ {_ -}P + ADP \overset{Aldolase}{\longrightarrow} Glyceraldehyde + DHAP + (ADP) \overset{Triose\ kinase}{\longrightarrow} Glyceraldehyde ^ {_ -} 3 ^ {_ -} P + ADP
$$
DHAP: Dihydroxyacetone phosphonate
Moannose
Moannose $\to$ Glucose-6-P
Polysaccharides
Digestion: Polysaccarides $\to$ oligosaccharides $\to$ disaccharides
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Oxidative
$$
Glucose^ {_ -}6^ {_ -}P + 2NADP^ + \to Ribose^ {_ -}5^ {_ -}P + 2NADPH
$$
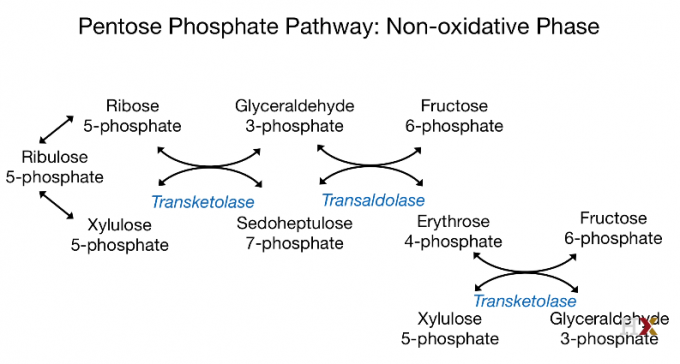
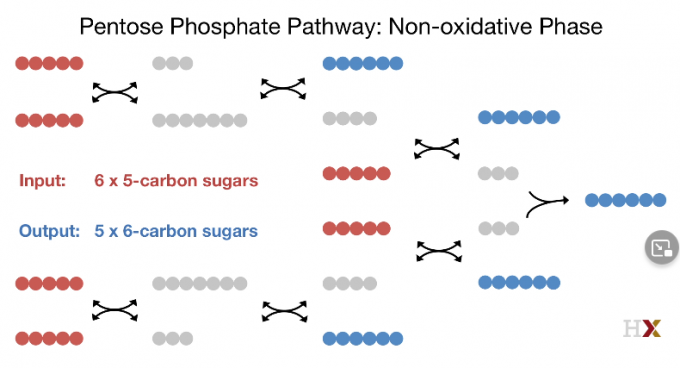
Non-oxidative
$$
Ribose^ {_ -}5^ {_ -}P \overset{Transketolase}{\longrightarrow}
\ \ \overset{Transaldolase}{\longrightarrow}
Fructose^ {_ -}1,6^ {_ -} 2P
$$
NADPH = Reducing potential
- Fatty acid synthesis
- ROS neutralization
Ribose-5-P $\to$ PRPP $\to$ Nucleotide synthesis
 |
|---|
 |
| © HarvardX |
Medical Consequence
NADPH is used to turn oxidized Glutathione to reduced Glutathione.
Glutathione could reduce the H2O2 and hemoglobin aggregates.
G6PD Deficiency
Glucose-6-P Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Deficiency
 |
|---|
| © PDB:1DPG |
$$
Glucose-6-P \overset{Glucose-6-P Dehydrogenase}{\longrightarrow} 6-Phosphoglucono-\delta-lactone
$$
This enzyme was made by dimer. N-terminal is the site of the NADPH interactive center. $\alpha$ and $\beta$ domains are keeping the dimer structure.
The deficiency of this enzyme
Red blood cells encounter oxidative stress - a large amount of iron & hemoglobin, highly oxygenate tissue
- lack mitochondria
- Dependent on the pentose phosphate pathway for reducing agents
Hemoglobin aggregates lead to the formation of Heinz bodies that affect the elastic properties of red blood cells and also contribute to hemolysis.
Heinz bodies:
- Heinz bodies (Heinz-Ehrlich bodies)
- Inclusions within red blood cells composed of denaturing hemoglobin
- The hallmark of G6PD deficiency
| Classes | Result |
|---|---|
| I | - Extreme deficiency - chronic haemolytic anaemia |
| II | - Severely deficiency (1-10% residual activity), acute haemolytic anaemia |
| III | - Moderately deficient(10-60%) |
| IV | - Normal activity (60-150%) |
| V | - Increased Activity(>150%) |
X chromosome linked Gene
Discovery
- Soldiers received Primaquine, an anti-malarial drug that adds oxidative stress to blood cells
- Some became anemic - had G6PD deficiency.
- Leading Acute hemolytic anemia (AHA)
Primaquine induces lethal oxidative damage to different strains of Plasmodium. In healthy people, the oxidative damage could be prevented by the reduced Glutathione
Factors affecting the severity of AHA:
- G6PD Activity
- Red Cell Aging
- Drug dose
Prevention
Triggering Agents
- Drug
- Ingestion of Fava Bean
- Infection
- Diseases like diabetes, myocardial infraction
- Intense physical exercise
Severe neonatal jaundice
- neurological consequences
- The peak of bilirubin in the blood due to accumulation of hemoglobin breakdown (hallmark)
Favism
- Fava beans contain high concentrations of:
- Nonvolatile glucosides (vicine, convivine)
- Aglycones: Produce free radicals
- Can trigger a hemolytic response in G6PD-deficient people.
Cures for G6PD Deficiency
- The most important measure is prevention - avoidance of the drugs and foods that cause hemolysis
- In severe cases of hemolysis, blood transfusions might be necessary, or even dialysis in acute renal failure.
- Some patients benefit from the removal of the spleen as red blood cells are lysed there.
The distribution of the G6PD is correlated to the distribution of malaria, which leads to a hypothesis that the G6PD is a selective advantage in parts of the world.
Principles of Biochemistry 23 |Carbohydrate metabolism| Class Notes |HarvardX
https://karobben.github.io/2021/06/22/LearnNotes/edx-biochm-23/









