15 Nuclear Receptors|Tulane
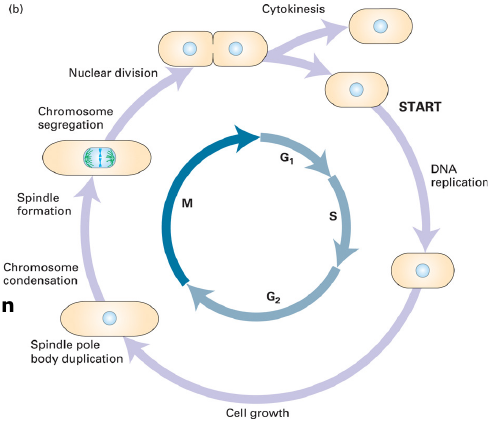
Cell Cycle
- Cell cycle phases
- Determining Cell cycle position
- Synchronous cells
Cell cycle:
- Grow, replicate, segregate chromosomes; Divide
Cycle Phases
The fate of a single parental chromosome throughout the eukaryotic cell cycle.
-
Mammalian cell expsaple:
G1 = 9, S = 10; G2 = 4.5; M = 0.5 -
G1 cells monitor environment and dize
-
G2 completion of DNA syntehsis
-
G0 Uncommitted to the cell cycle
-
The cell cycle in yeast takes about 90 min.
M phase:
- Prophase – chromosomes condense, spindle forms, envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase – kinetochores attach to spindle, chromosomes align.
- Anaphase – chromosomes separate.
- Telophase – chromosomes reach spindle poles, decondense chromosomes, spindle breaks down and envelope forms.
Monitoring cell cycle position
- Microscopy
- Count cell number
- Hemocytometer
- Cell counter
- Viability assay
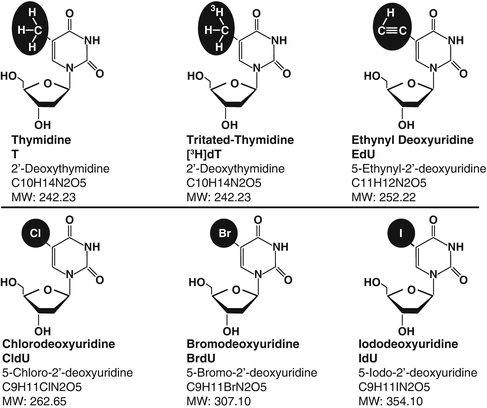
- DNA labeling
Tritiated thymidine, Br-dU, EdU - DNA content
- Yeast morphology
- Cell cycle regulated protein and mRNAs
Microscopy
-
Microscopy
-
Hemocytometer
Whit the cover slip in place transfer a small amount of the cell suspension to the edge often cover slip and allow the chamber to fill by capillary action, Trypan blue (or, Eosin, Propidium) staining can distinguish live from dead cells. -
Cell Counter
-
Viability assay
Basically, viability means how many cells are living.
But viability doesn’t tells more. So, there are more specific assays like, apoptosis assay, proliferation assay, and function assay. MTT Assay.
| Hemocytometer |  © Abishek Vembadi, et al |
| Cell Counter |  © acmerevival |
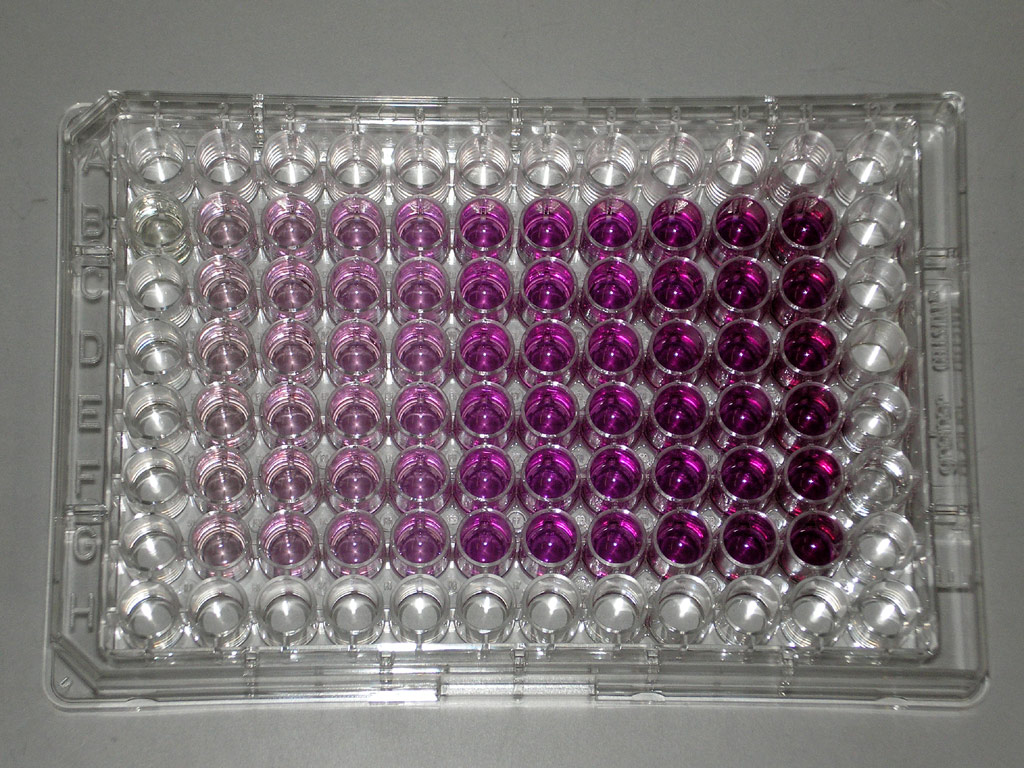
Viability assay: MTT Assay
Principle
Water soluble yellow MTT
Reduced to purple insoluble formazan by mitochondrial dehydrogenases
Water insoluble formazan can be solubilized using isopropanol or other solvents
The dissolved material is measered spectrophotometrically yielding absorbance as a function of concentration of converted dye.
Mitochondrial Dehydrogenase catalize the Yellow MTT to purple insoluble form
 |
|---|
 |
| © wikipedia |
Video Protocol: Abnova: MTT Assay; 2010
Why MTT assay: Though dyes like Trypan blue could mark living cell based on the intact cell membrane, but can’t tell which cell are dying.
MTT Tetrazolium Reduction Assay, which is a colorimetric assay.
Cellular oxidoreductase enzymes reduce the terazolium dye MTT bromide to its insoluble form ozone which has a purple color, quantity was based on the changes in absorbance at 570nm using a spectrophotometer. As a result, it can be used to measure cytotoxicity loss of viable cells or cytostastic activity shift from proliferation to quiesence of potential medicinal agents and toxic materials.
Advantage: Fewer steps, uses fewer materials, and does not carry the added burden of radioactive waste disposal.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for suspending cells,
- Must be optimized for seeding amount and assay duration to obtain satisfactory results
- Precipitated protein and cellular debris present in the cell culture plate wells may interfere with the optical ratings
Creative Bioarray[1]
MTS: adding into culture media directly. (expensive)
MTT, MTS, CCK-8, SRB
Significance:
Tetrazolium dye reduction is assumed to be dependnet on NAD§H-dependent oxidoreductase enzyme. The sensitivity of the cell group are different from each other. Proliferation cells shall more sensible then because of it’s high metabolic rate.[2]
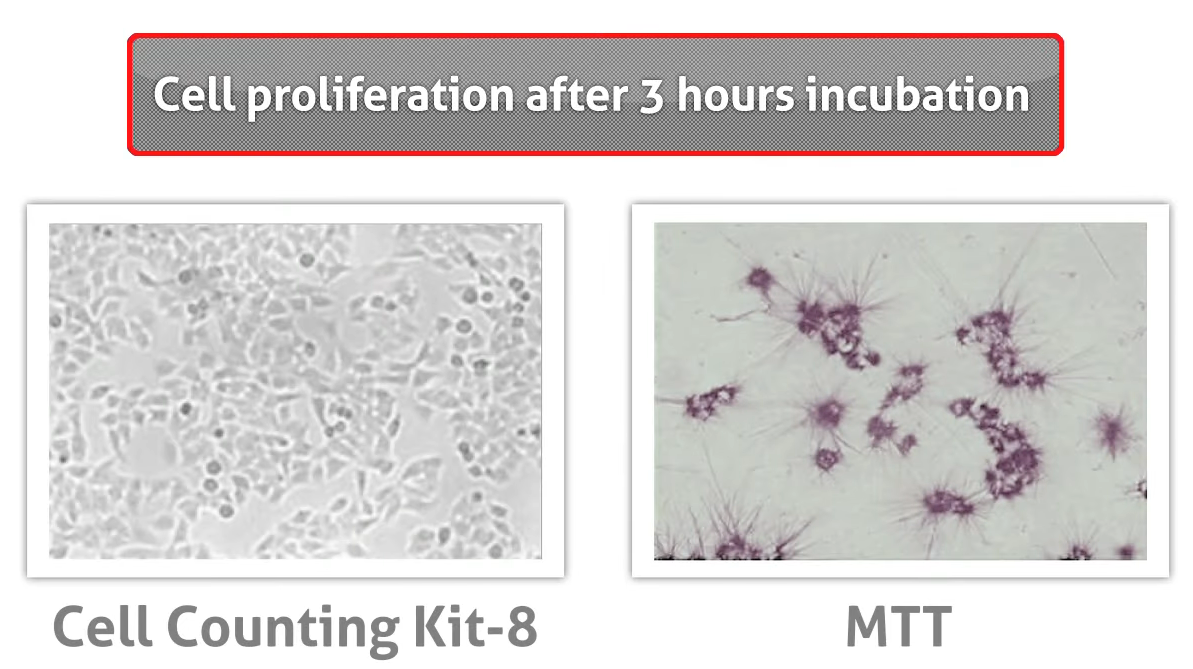
PS: alternative Assay: CCK-8
Not like MTT, which using organic solution and toxic to Cell, which effect the function, reproduction, and change the morphology of the cell, CCK-8 was more temperate.[3]
 |
|---|
| [© Biocompare[3:1] |
Monitoring cell cycle position
- Microscopy
- Count cell number
- DNA labeling - tritiated thymidine, Br-dU, EdU
[3H]thymidine ([3H]dT)

|© Anthony N. Karnezis, et al|
 |
|---|
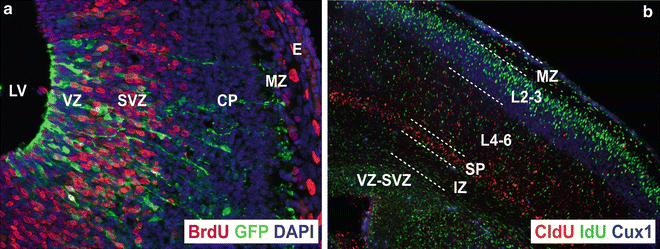 |
 |
| © Alvaro Duque |
Monitoring cell cycle position
Yeast Morphology change
 |
 © Pierre Delobel, et al |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| © Kathleen Scheffler, et al | © Davide Tamborrini, et al |
Synchronizing cells for cell cycle studies
- Drugs - Aphidicolin (G1), hydronxyurea(S), nocodazole(M), serum starvation(G1), mimosine
- Mitotic shake-off
- Centrifugal elutriation
- Embryonic cells
- Yeast
Drugs
Aphidicolin (G1)
hydronxyurea(S), nocodazole(M), serum starvation(G1), mimosine
| Header One | Header Two |
|---|---|
| Aphidicolin | Aphidicolin is a tetracyclic diterpenoid first produced by the fungus Cephalosporium aphidicola. This antibiotic is a potent inhibitor of cellular DNA synthesis by targeting α, ε, and δ DNA polymerases in eukaryotic cells lines with little to no effect on β or γ DNA polymerases. Studies have shown that Aphidicolin specifically binds to α DNA polymerase, resulting in the formation of a pol α-DNA-aphidicolin ternary complex that blocks DNA replication. The uses for this compound include synchronized cells at the G1/S boundary and increased gene amplification.[4] |
| Hydronxyurea | The therapeutic effect is generally believed to be due to the suppression of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), which slows DNA polymerase movement at replication forks and induces an S phase cell cycle arrest in proliferating cells.[5] |
Mitotic shake-off Adherent cells round up in mitosis
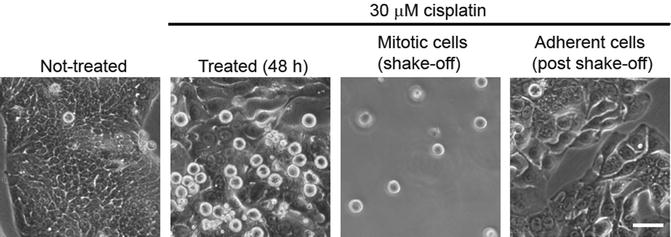 |
|---|
| © Lucy H. Swift, Roy M. GolsteynEmail |
Centrifugal Elutriation
| © Fredrik B Thorén |
Synchronization of cells and nuclei is a powerful technique for the exact study of regulatory mechanisms and for understanding cell cycle events. Counterflow centrifugal elutriation is a biophysical cell separation technique in which cell size and sedimentation density differences of living cells are exploited to isolate subpopulations in various stages of cell cycle.
This cell separation technique is available since 1948. Centrifugal elutriation offers the advantage that it does not perturb the cell cycle progression; it selects uniformly sized cells, as the cell size generally correlates with cell cycle stage. The major advantage of centrifugal elutriation is that it permits the selection of cells during the whole cell cycle. Among the disadvantages of elutriation, the moderate dispersion of synchrony could be mentioned in fractions collected at the end of the elutriation process, especially in the late S, G2 and M phases. Best synchrony with elutriation is achieved in G1 and in early and mid S phase. Nevertheless, this method is still regarded as one of the best ways of preparing ‘unperturbed’ synchronous yeast cultures for cell cycle studies. Analysis of the DNA distributions after centri- fugal elutriation confirmed that excellent synchrony was obtained with low dispersion throughout the cell cycle.
Source: Gaspar Banfalvi
What is the evidence for cell cycle control
- Fuse a mitotic cell with any other cell drives it into mitosis.
- Fuse a S phase cell with one in G1 – both are in S- incorporate labeled nucleotides.
- Fuse a G2 cell with one in S – S continues to replicate, but no DNA synthesis in G2 cell.
Diffusable factors are the cell cycle engine, which is conserved from yeast to man.
Fusing cell???

Oocyte Maturation
The oocyte is 4C. What is the DNA content after each step?
Step 1 requires protein synthesis
How can you use the frog oocyte to assay for MPF???
MPF from yeast to man works in the oocyte injection assay
MPF activity in frog development
The embryonic cell cycle of xenopus laevis
Cleavage without growth- 12 consecutive mitoses – no RNA synthesis Oocyte stockpiles materials for multicellular embryo
The frog embryonic cycle is regulated by a biochemical oscillator
• Fertilize frog eggs and they divide.
• Block spindle assembly with nocodazole – fertilized egg still oscillates.
• Block DNA synthesis with aphidicolin – still oscillates.
• Inhibit protein synthesis with cycloheximide – embryos will not divide after fertilization.
• Oscillation occurs in the absence of a nucleus.
• Inhibit protein synthesis and inject MPF – embryos enter mitosis.
Downstream events (chromosome decondensation and DNA synthesis) regulated by the destruction of MPF in embryonic cells.
Fertilization leads to rapid inactivation of MPF.
Identifying the oscillator
Why does the cell cycle engine oscillate?
Protein degraded at onset of anaphase. Tim Hunt showed that a subunit of MPF had this protein – cyclin B
Xenopus egg extract
Electrically activate xenopus eggs- prepare extract and add sperm nuclei. Replication occurs, chromosomes condense and nuclei form in cyclic fashion. Inhibit protein synthesis and extract stops cycling. Add antisense RNA to cyclin B – stop cycling. Non-degradable cyclin B mRNA lacks 90 a.a. from N-terminus. Cyclin accumulates before MPF is detected. Accumulate cyclin B to high levels and destroy.
Yeast mitotic cycle
Yeast must repondto size, food and sex-START. Somatci cells must grow and reach a certain size before division
- Cycles in 90 mins
- Grows in simple medium
- Well-defind genertics
- Size of bud r lenghth defines cell cycle position
Schizosaccharomyces pombe – fission yeast;
Saccharomyces cerevisiae – budding yeast.
The G2 checkpoint is more prominent in pombe.
The fission yeast
G1: short
S: Relativily short
G2: Longest
Conditional mutants
- product fails only under certain conditions. ts mutants unable to grow at restrictive temperature.
- 35-37 °C: restrictive; 20-23 °C: permissive
- cdc (cell division cycle) ~70 known arrest at a single point in the cell cycle at the non-permissive or restrictive temp. Discovered by Lee Hartwell.
- S. pombe grows only in length. Cdc-ts arrests in G2 at nonpermissive temperature. Transfect in library to restore temperature resistant growth.
- Cdc2 identified by complementation. Cdc13 also required for entry into mitosis.
- Cdc2 sequence reveals a protein kinase.
Wild-type cell division cycle (CDC) genes can be isolated from a S. cerevisiae genomic library by functional complementation of cdc mutants.
The budding yeast S. cerevisiae: Antibody to cdc2 immunoprecipitates MPF. MPF is a heterodimer of cdc2/cdc13 with protein kinase activity. Cdc13 has homology to cyclin B. Cerevisiae cdc-28 complements cdc2 mutants.
Cdc28 vs Cdc2
Cdc28 mutant blocks cells before S phase-continue to grow,
but
• 1. Don’t replicate DNA.
• 2. Don’t duplicate spindle poles.
• 3. Don’t bud.- Defines a point in the cell cycle as START.
• G1 checkpoint –nutrients; G2 checkpoint chromosomes.
A single protein overcomes G1 and G2 checkpoints.
S. pombe grows with a haploid DNA content – selective
pressure for G2 arrest. Why?
Creative Bioarray, Comparison of Different Methods to Measure Cell Viability, Youtube ↩︎
Biocompare, Watch Animation: DOJINDO CCK-8 Assay vs. MTT Assay, 2011, Youtube ↩︎ ↩︎
Xu, Yong-Jie et al. “Hydroxyurea Induces Cytokinesis Arrest in Cells Expressing a Mutated Sterol-14α-Demethylase in the Ergosterol Biosynthesis Pathway.” Genetics vol. 204,3 (2016): 959-973. doi:10.1534/genetics.116.191536 ↩︎
15 Nuclear Receptors|Tulane
https://karobben.github.io/2021/11/15/LearnNotes/tulane-cellbio-15/