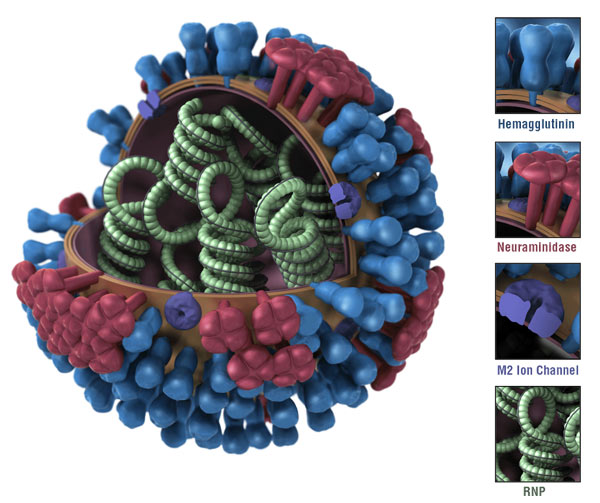
Influenza
Resources
- YouTube:
- Michael Vahey: Phynotypic Variability and Plasticity in Influenza A Virus; 2019; UC Berkeley
- Nicholas Wu: Influenza Evolution: A Major Challenge in Vaccine Development; 2021; UIUC
- Paul Genecin: The Exam Room: Influenza & the Vaccine Evaluation; 2015; Yale School Of Medicine
- Paul Van Buynder: Current controversies with influenza vaccines: hope for the future?; 2016; Simon Fraser University
- 3D animation for influenza life circle; 2014; Nucleus Medical Media
- 3D animation for influenza life circle; 2020; XVIVO Scientific Animation
- Influenza Virus Microbiology Animation (more detailed on mechanism); 2020
- James McSharry: Influenza Viruses by James McSharry, PhD; 2017
- Paper:
Basic Information
 |
|---|
| Figure 9 Flint et al. 2004 ASM Press |
Influenza A gets the most number of variance. They are named based on the subtype of the surface protein HA and NA. For example, H1N1, H3N2, H5N1, etc. For HA, there are 18 subtypes (H1-H18), For NA, there are 11 subtypes (N1-N11)
They are transmitted by respiratory droplets. The virus can survive on surfaces for 24-48 hours. The virus can be transmitted before the symptoms show up.
Morphalogy of the Influenza Virus
 |
|---|
| Unlike the Zika virus, it has a uniform on size and shape. The surface protein alos aligned with recognizable patterns. In the resconstructred influenza, it has heterogeneous progeny, the surface protein HA (green) and NA (yellow) distributed by random. |
What’s the advantages of the heterogeneous progeny? Influenza’s enter and release is based on the 2 main surface protein, HA an NA. By changing the morphalogy of the virus, it could regulate the ratio and distribution of the HA and NA to fit the environment.
Segmented Genome
 © wikipidia © wikipidia |
|---|
| Unlike the Zika virus, the influenza virus has a segmented genome. The segmented genome allows for reassortment of genes between different strains of the virus, which can lead to the emergence of new strains with different properties. This is one of the reasons why influenza viruses are able to evolve rapidly and evade the immune system. |

Influenza causing pandemic almost every 2 years.

Increased the glycosylation of the HA protein. This glycosylation change help the virus to evade the immune system.
Treatment
 |
|---|
| © Yanbai Li, et al; 2024 |
Ion Channel Blockers
These drugs target the M2 ion channel protein in influenza Type A viruses. By blocking this channel, they prevent acidification inside the viral particle, which is necessary for uncoating and releasing the viral RNA.
- Amantadine – Effective only against influenza A viruses.
- Rimantadine – Also active against influenza A only, with a slightly better side effect profile than amantadine.
⚠️ Note: Many influenza A strains have developed resistance to these drugs, limiting their current use.
Neuraminidase Inhibitors
These medications block the neuraminidase enzyme, which is required for the virus to release new viral particles from infected cells. They work against both influenza A and B.
- Oseltamivir carboxylate (Tamiflu) – An oral drug that inhibits neuraminidase in both influenza A and B.
- Zanamivir (Relenza) – An inhaled version that also targets both influenza A and B.
These drugs are most effective when taken within 48 hours of symptom onset.
PA Inhibitors
- Baloxavir marboxil (Xofluza) – A newer antiviral that inhibits the PA protein of the influenza virus, preventing viral replication. It is effective against both influenza A and B viruses.
HA Stem Inhibitors
- Arbidol – A broad-spectrum antiviral that targets the hemagglutinin (HA) protein of the virus. It is thought to inhibit the fusion of the viral envelope with the host cell membrane, preventing viral entry.
⚠️ Note: Arvudol is not FDA-approved for influenza but is used in some countries like Russia and China.
Monoclonal Antibodies
All the monoclonal antibodies are not FDA-approved for influenza. They are still on clinical trials.
| Name | Binding to | IC50 (μg/mL) | 100% protection in vivo | Adverse event | Usage | Clinical studies | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR6261 | HA-stalk (H1, H2, H5, H6, H9, H13, and H16) | 0.12–14.87 | Pre: 5 mg/kg Post: 15 mg/kg | −a | Intravenous | I NCT01406418, February 2013 to November 2013; II NCT02371668, February 2015 to November 2018 | (149–153) |
| CR8020 | HA-stalk (H3, H4, H7, H10, H14, and H15) | 1.1–13.1 | Pre: 3 mg/kg Post: 15 mg/kg | − | Intravenous | I NCT01756950, January 2013 to November 2013; II NCT01938352, October 2013 to January 2014 | (150) |
| VIS410 | HA-stalk (H1, H2, H3, H5, H6, H7, and H9) | 0.3–11 | Post: 2.5 mg/kg | Mild diarrhea | Intravenous | I NCT02045472, September 2014 to May 2015; II NCT02989194, January 2017 to October 2017 | (154–157) |
| MHAA4549A | HA-stalk (H1, H2, H3, H5, and H7) | 1.3–45.1 | Post: 100 and 900 µg | Headache | Intravenous | I NCT01877785, July 2013 to November 2013; I NCT02284607, November 2014 to March 2015; IIa NCT01980966, November 2013 to June 2014; IIb NCT02293863, January 2015 to May 2017 | (158–161) |
| MEDI8852 | All HA-stalk | 0.064 | Pre: 1 mg/kg Post: 10 mg/kg | Headache, hypoglycemia, and bronchitis | Monotherapy | I II NCT02350751, December 2015 to December 2016 | (162, 163) |
| TCN-032 | M2e (H1, H2, H3, H5, H7, andH9) | − | − | − | Monotherapy | I NCT01390025, September 2011 to March 2012; II NCT01719874, August 2012 to March 2013 | (145, 164) |
| 1G01 | N1-N9 NA and IBV NA | 0.01–2 | Pre: 0.3 mg/kg Post: 5 mg/kg | − | − | − | (129) |
Vaccine
The circulating of the influenza: H3N2 (60%), H1N1 (15%), B (25%). (Paul Van Buynder; 2016)
For influenza A, technically, the antigenic drift make leads to epidemic, but the antigenic shift is the one that leads to pandemic.
Influenza B only causes epidemic, not pandemic.
For influenza vaccine, there are:
- SD-IIV: Standard-dose, for most people (most common)
- HD-IIV: High-dose, for elderly (more antigens)
- LAIV: Live attenuated, nasal spray
- aIIV: Adjuvanted, for stronger immune response
- ccIIV: Cell culture-based
- RIV: Recombinant Influenza Vaccine.
IIV = Inactivated Influenza Vaccine (the virus is killed, not live)
Limitation of the Vaccine
- Predicted sub-strains
Unlike other vaccine, because the flu happens almost every year, getting the vaccine is suggested before each flue season.
The sub-strain of the virus are predicted based on the previous year. So, the vaccine only getting around 60% of protections. - Egg-based vaccine
95% of the vaccine are made from eggs. Birds’ sialic acid connection is slightly different from human’s. When the influenza virus infects the eggs, they would mutates to adapt to the eggs. This could lead to a mismatch between the vaccine and the circulating virus.