WGCNA Tutorial 2
WGCNA Tutorial 2
Official Website
Paper: Peter Langfelder, 2008
Weighted correlation network analysis (WGCNA) can be used for finding clusters (modules) of highly correlated genes, for summarizing such clusters using the module eigengene or an intramodular hub gene, for relating modules to one another and to external sample traits (using eigengene network methodology), and for calculating module membership measures.
Play list for Network Analysis
Install
|
Data:
1. Data Preparation
1.1 Loading DataSet
The data sets contain roughly 130 samples each. Note that each row corresponds to a gene and column to a
sample or auxiliary information.
|
1.2 Groups in List
|
1.3 Rudimentary data cleaning and outlier removal
Check that all genes and samples have sufficiently low numbers of missing values.
|
1.4 Cluster
|
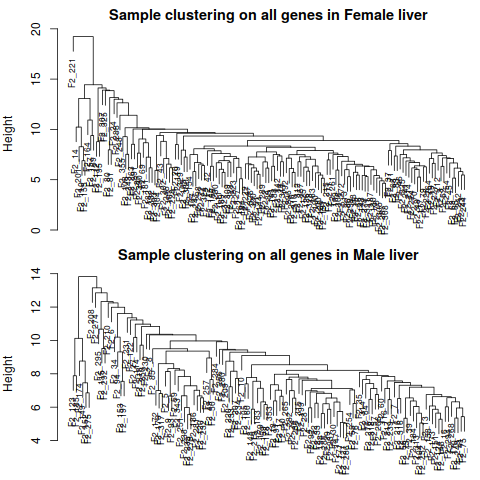
By inspection, there seems to be one outlier in the female data set, and no obvious outliers in the male set. We
now remove the female outlier using a semi-automatic code that only requires a choice of a height cut
1.5 Remove Outlier
|
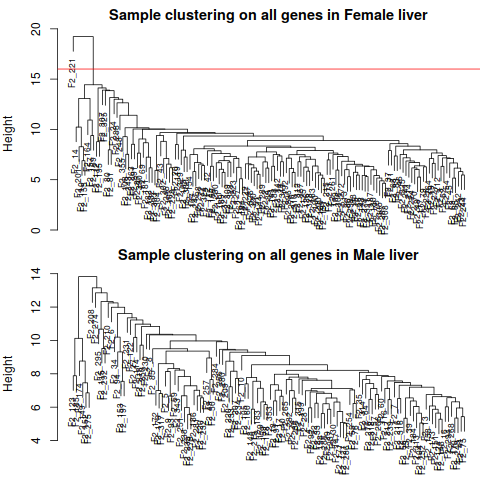
1.6 Loading Clinical Trait Data
|
2. Network Construction and Module Detection
graph LR; START(Network construction) Net1(one-step network construction) Net2(Step-by-step network construction) Net3(automatic block-wise network construction) START-->|Minimum Effort|Net1; START-->|Customized/Alternate Methods|Net2; START-->|Large Data Set|Net3;
2.1 One-Step Network Construction and Module Detection
|
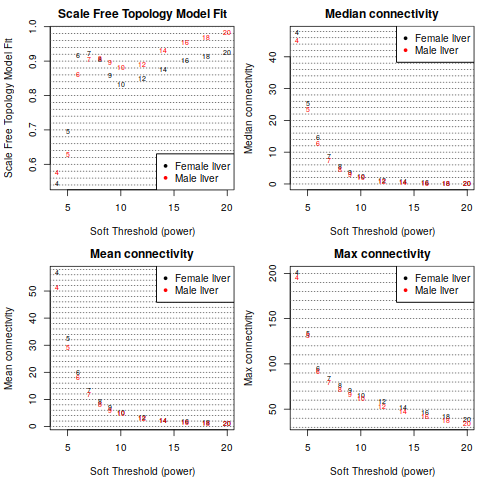
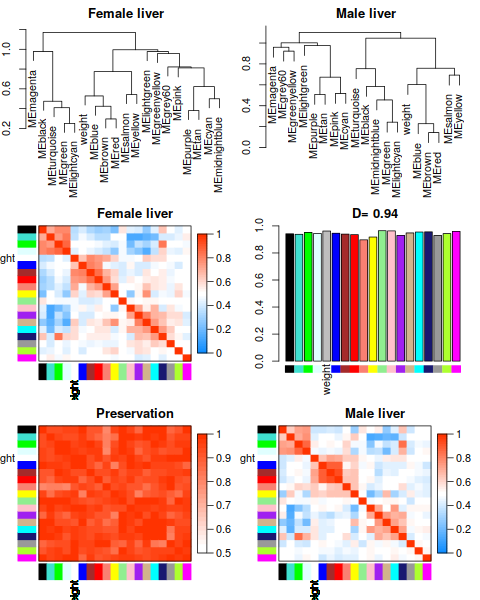
2.2 Network construction and consensus module detection
Attention: We have chosen the soft thresholding power 6, minimum module size 30, the module detection sensitivity deepSplit 2, cut height for merging of modules 0.20 (implying that modules whose eigengenes are correlated above 1 − 0.2 = 0.8 will be merged), we requested that the function return numeric module labels rather than color labels, we have effectively turned off reassigning genes based on their module eigengene-based connectivity KME, and we have instructed the code to save the calculated consensus topological overlap.
In this example most of them are left at their default value. We encourage the user to read the help file provided within the package in the R environment and experiment with tweaking the network construction and module detection parameters. The potential reward is, of course, better (biologically more relevant) results of the analysis.
|
2.3 Model Extract
|
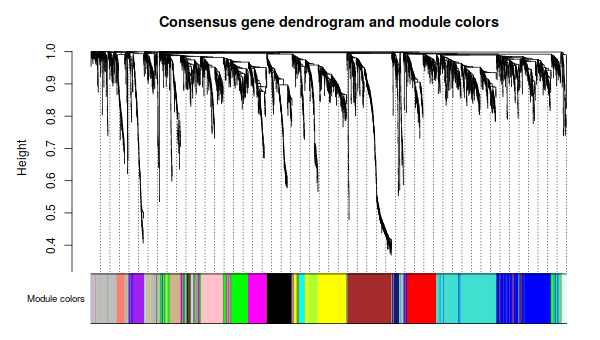
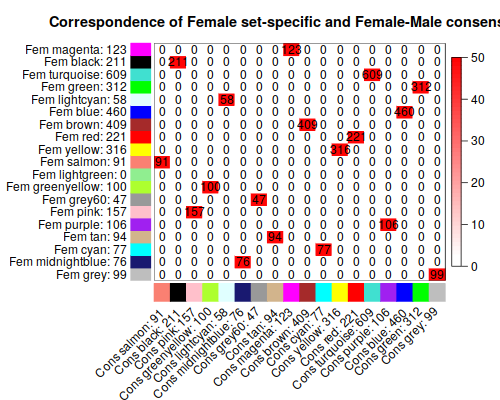
3. Relating the consensus modules to female set-specific modules
3.1 datExpr
(WGCNA Tutorial 1, 1-2)
|
3.2 Relating consensus modules to female set-specific modules
|
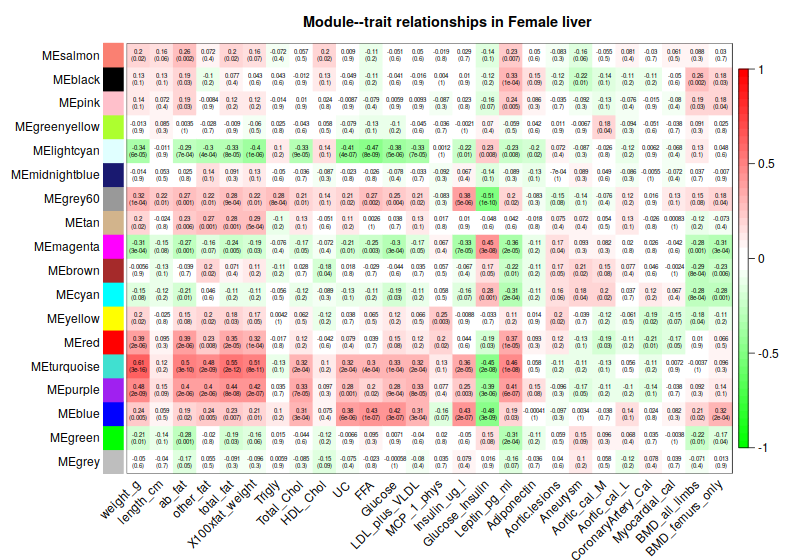
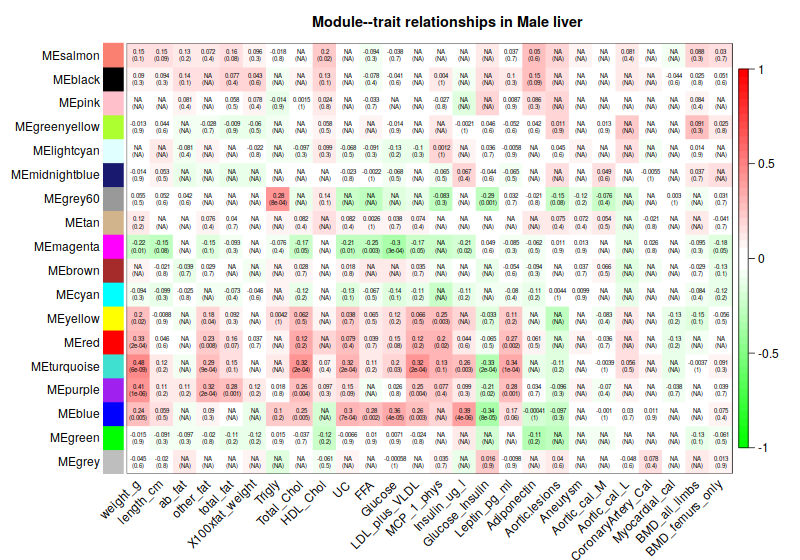
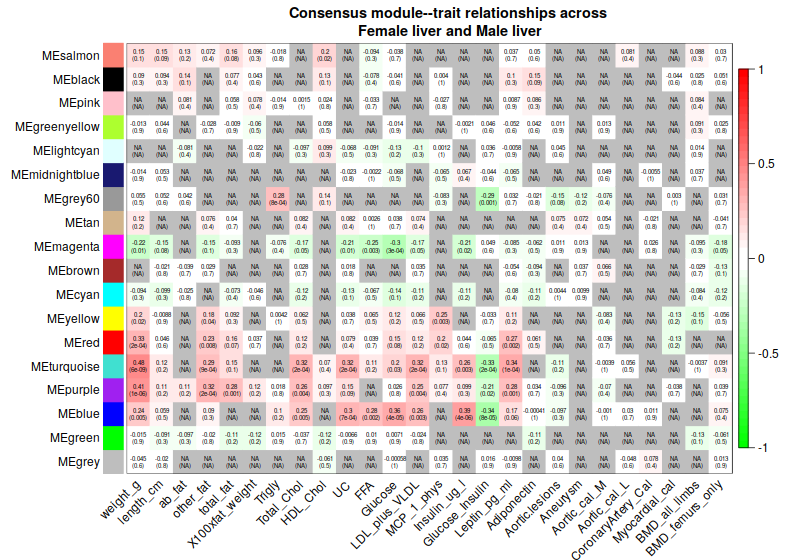
4. Consensus module to traits
4.1 Correlation
|
|
|
4.2 Exporting results of the network analysis
|
5. Relationships among modules and traits
|
WGCNA Tutorial 2








