from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import xgboost as xgb
from xgboost import plot_importance
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=1234565)
params = {
'booster': 'gbtree',
'objective': 'multi:softmax',
'num_class': 3,
'gamma': 0.1,
'max_depth': 6,
'lambda': 2,
'subsample': 0.7,
'colsample_bytree': 0.7,
'min_child_weight': 3,
'silent': 1,
'eta': 0.1,
'seed': 1000,
'nthread': 4,
}
plst = params.items()
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, y_train)
num_rounds = 500
model = xgb.train(plst, dtrain, num_rounds)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(X_test)
ans = model.predict(dtest)
cnt1 = 0
cnt2 = 0
for i in range(len(y_test)):
if ans[i] == y_test[i]:
cnt1 += 1
else:
cnt2 += 1
print("Accuracy: %.2f %% " % (100 * cnt1 / (cnt1 + cnt2)))
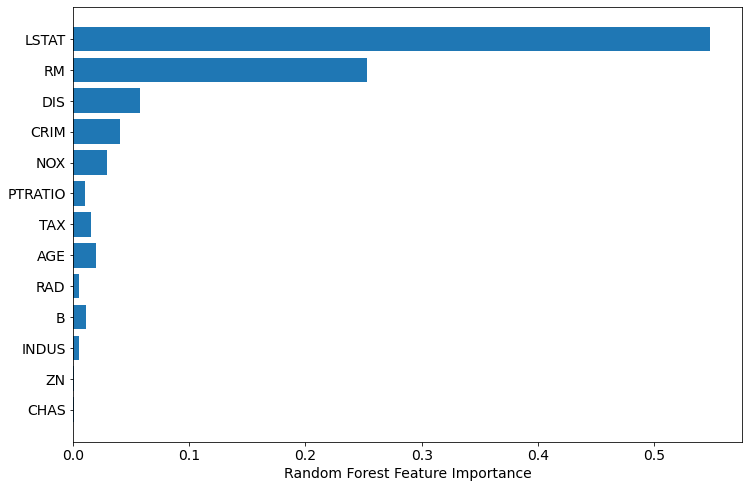
plot_importance(model)
plt.show()
|