Principles of Biochemistry 14 |Glycolysis in Bacterial| Class Notes |HarvardX
Aerobes Condition
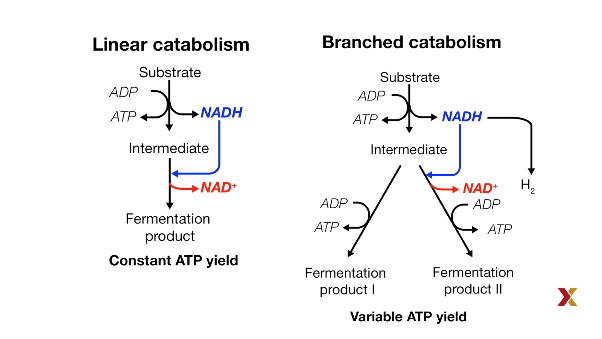
Metabolic pathways in becteria that operate with Low O2
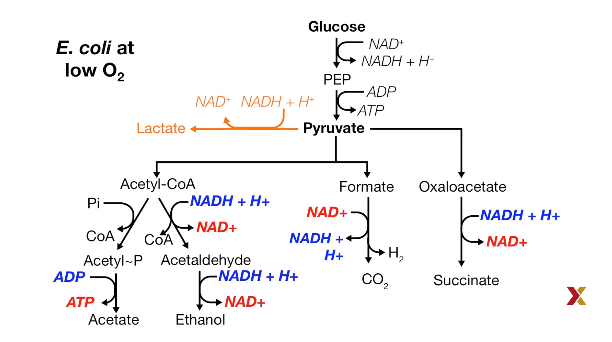
Exp: E. Coli
Multiple fermentation product:
For example, lactate, ethanol, acetate, citrate.
 |
|---|
| © HarvardX |
 |
|---|
| © HarvardX |
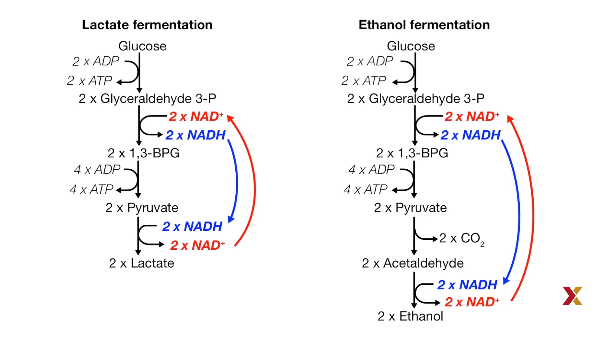
Fermentation Branches
 |
|---|
| © HarvardX |
Anaerobic Respiration and ATP
| Respiration Type | O2 | Electron Receptor | Product | $\Delta G (kJ/2e^ -)$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellular Respiration | O2 is sufficient | O2 | H2O | -219.07 |
| Fermentation | O2 is not used | Varieties | Varieties | |
| Anaerobic (Denitrifier)) | O2 is not used | NO3- | N2 | -209.46 |
| Anaerobic (Metal Reducer)) | O2 is not used | Fe3+ | Fe2+ | -206.12 |
| Anaerobic (Sulfidogen)) | O2 is not used | SO42- | HS- | -20/24 |
| Anaerobic (Mehtanogen)) | O2 is not used | CO2 | CH4 | -14.58 |
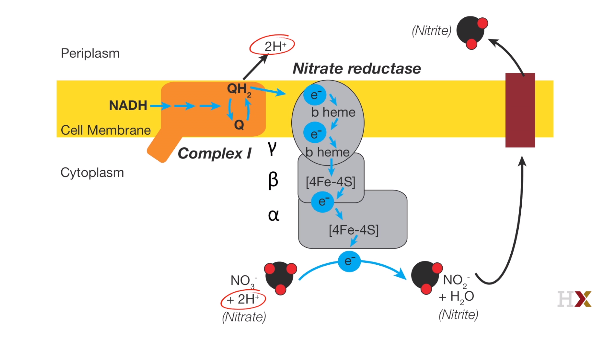
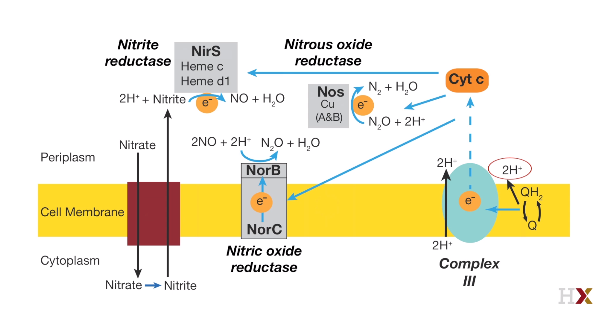
Dinitrifying
Fe^2+^: Ferrous iron hemoglobin Fe^3+^: Ferric iron methemoglobin$2NO_ 3 ^- + 12H^ + 10 e^ - \to N_ 2 + 6 H_ 2O$
$NO_ 3 ^- \to NO_ 2 ^-$ Nitrate to Nitrite
$NO_ 2 ^- \to NO$ Nitric oxide
$NO\ \ \to N_ 2O$ Nitrous oxide
$N_ 2O\ \to N_ 2$ Dinitrogen
| © HarvardX; Dinitrifying |
|---|
 |
 |
Bacterial and human health
The exist of bacterial:
Colonization:
- Begins at birth
- First from mother
- Then from environment
Diversity:
- Nutrient availability
- Physical/chemical environment
- Anti-microbial defenses
- Microbe interaction and modification of the local environment
Beneficial:
- Pathogen defence
- Metabolic function
- Immune system maintain
- Energy balance
Disrabtion:
Principles of Biochemistry 14 |Glycolysis in Bacterial| Class Notes |HarvardX
https://karobben.github.io/2021/04/28/LearnNotes/edx-biochm-14/









