Single Cell RNA-Seq Notes
Single Cell RNA-Seq Notes
Video materials: Human Cell Atlas: Day 1: HCA Latin America Single-Cell RNA-SEQ Data Analysis Workshop (Virtual)
Challenges
Barcodes errors
 |
|---|
| © Dana Pe’er 2021 |
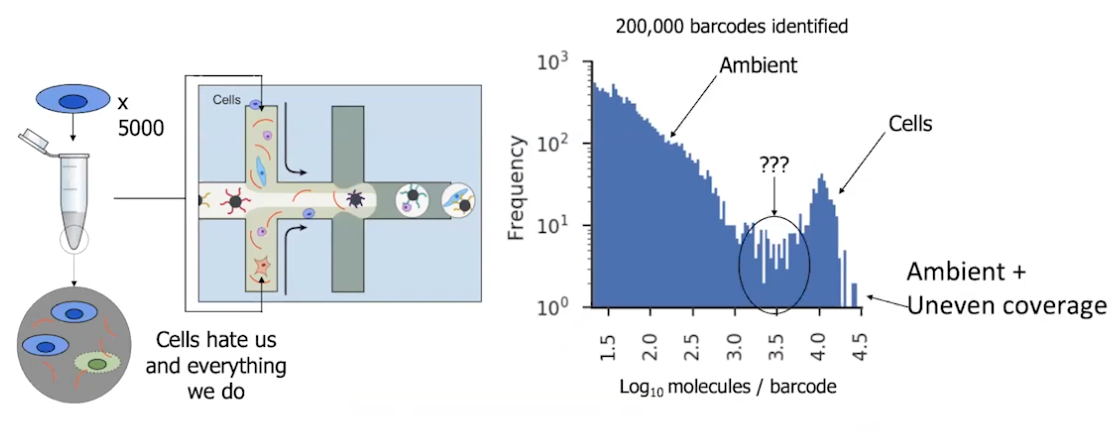
5000 cells in, but get 200,000 barcides identified.
Sbarcity
Sbarcity makes the noise is high and the protocols for bulk RNA-seq are not compectable for scRNA-Seq.
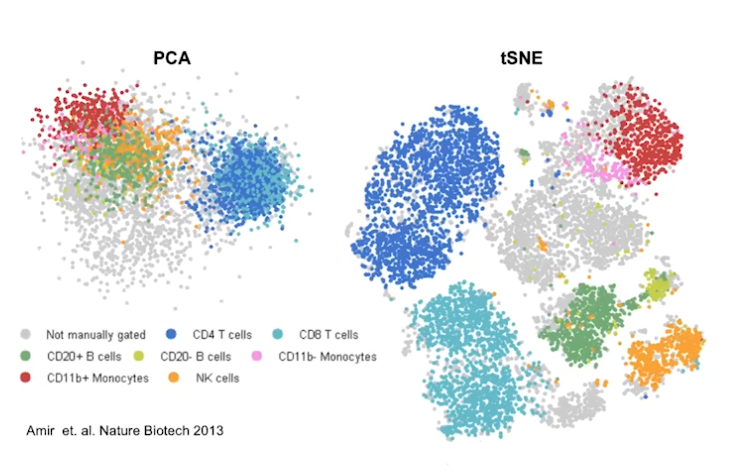
Demension
 |
|---|
| © Dana Pe’er 2021 |
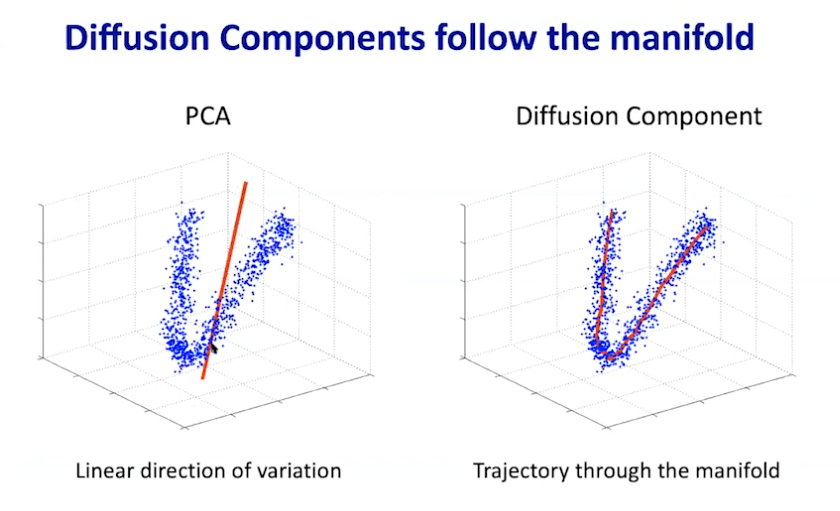
Reduce demention based on linear projection (PCA) is not compectable for hide dementional data
 |
|---|
| © Dana Pe’er 2021 |
Batch effects
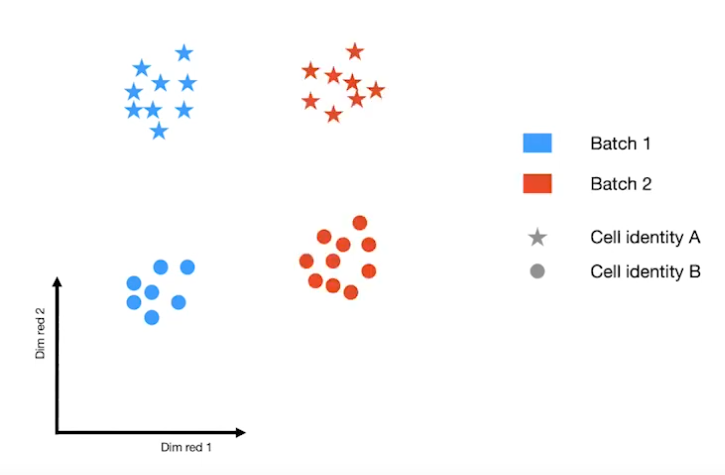 |
|---|
| © Dana Pe’er 2021 |
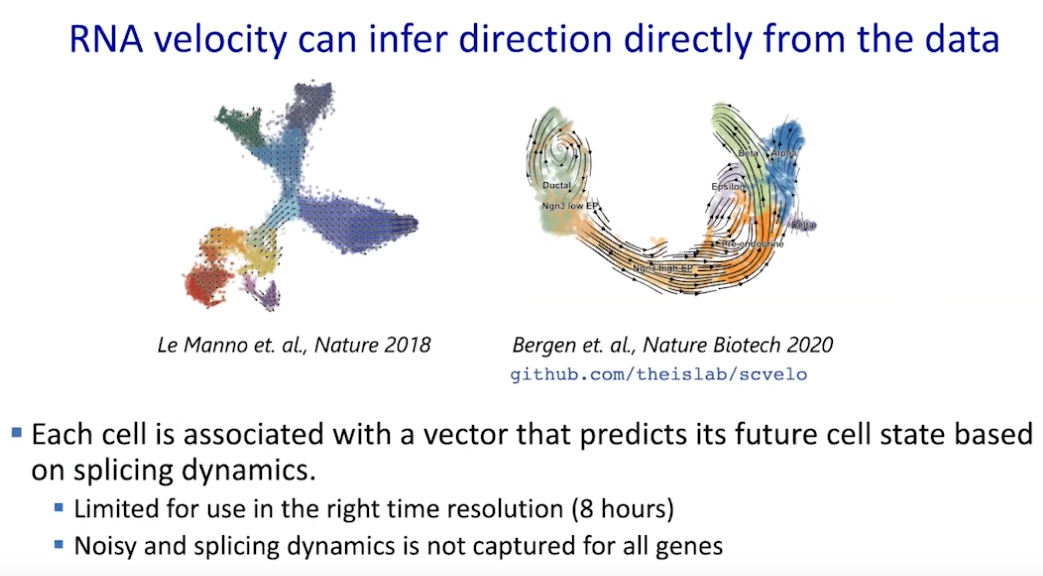
Path walk: psudotime
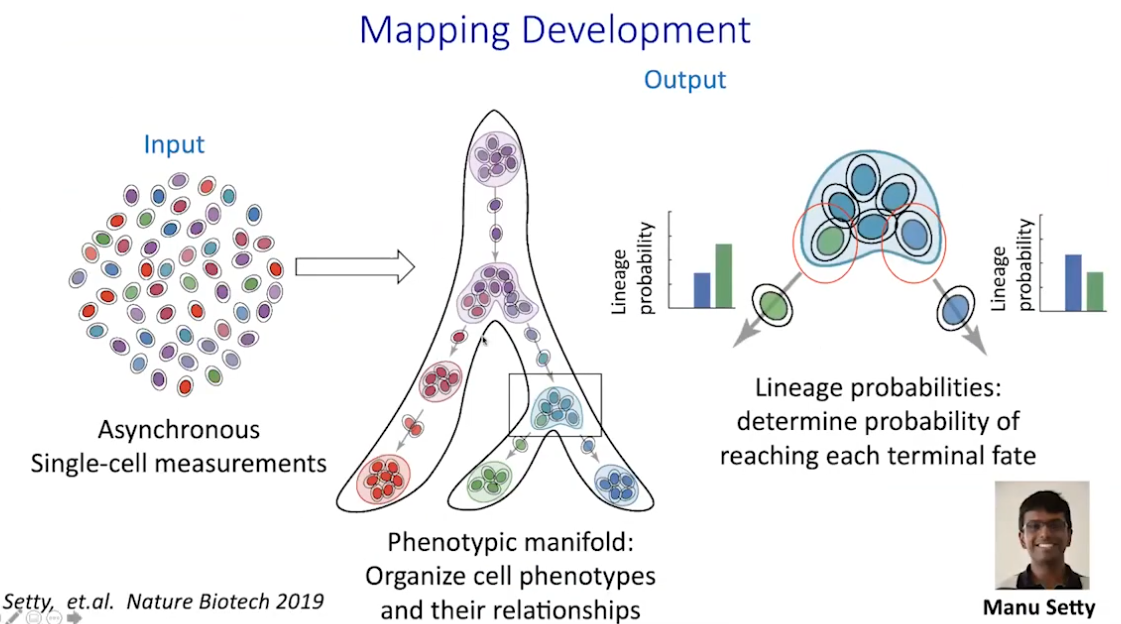 |
|---|
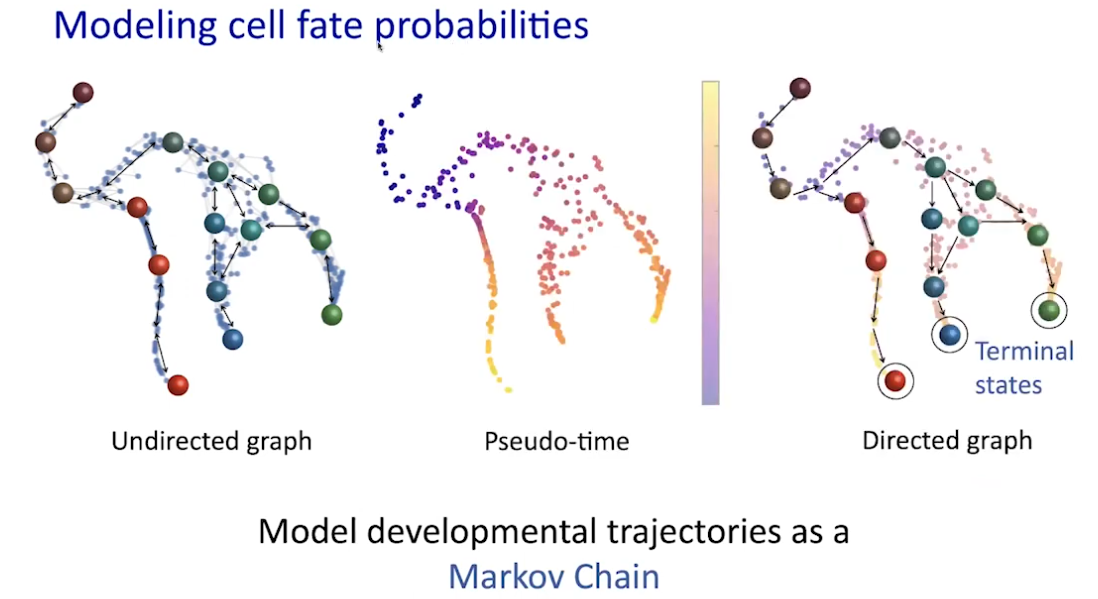 |
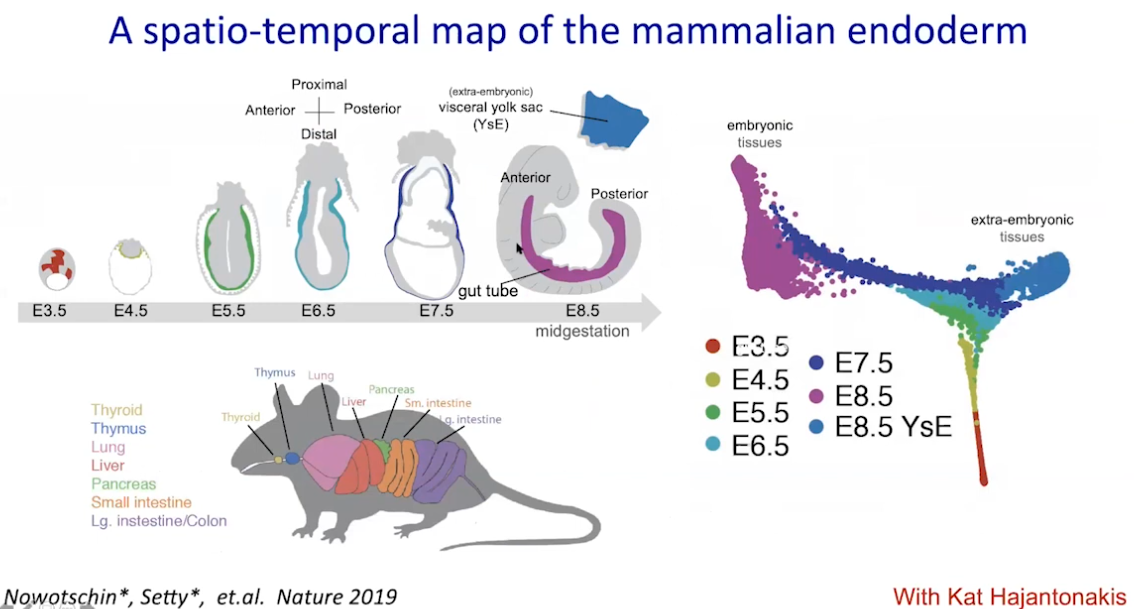 |
 |
 |
| © Dana Pe’er 2021 |
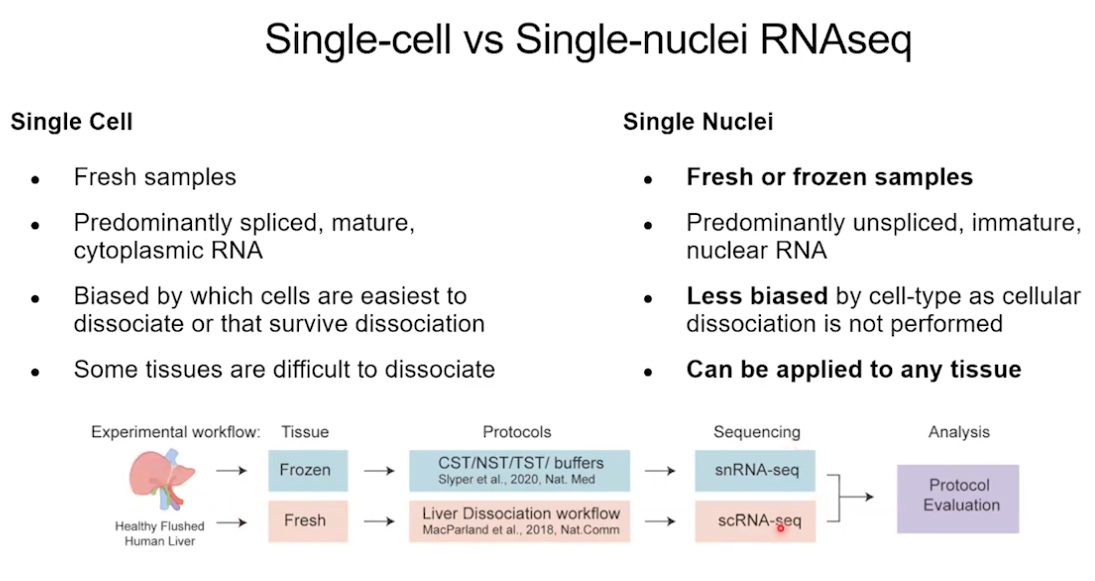
Nuclear RNS-Seq
Different between single cell RNA-Seq and single Nuclear RNA-Seq
 |
|---|
| © Dana Pe’er 2021 |
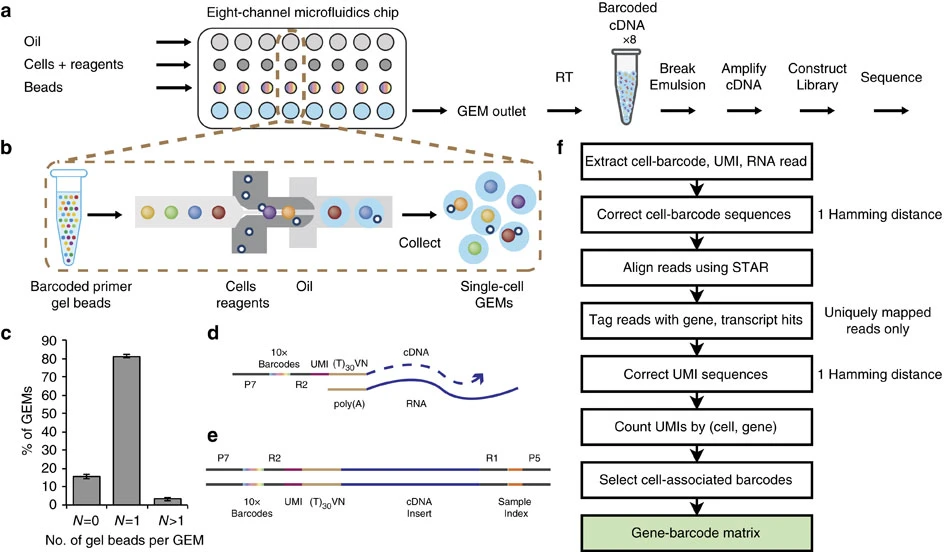
Chromium Next GEM Single Cell 5’ Reagent Kits v2 (Dual Index)
From: X10 Genomics
 |
|---|
| © X10 Genomics |
Gel Bead- Read 1 Barcode×16 UMI×10 TSO ×13 rGrGrG
- an Illumina R1 sequence (read 1 sequencing primer)
- a 16 nt 10x Barcode.
- a 10 nt unique molecular identifier (UMI)
- 13 nt unique molecular identifier (TSO) are released and mixed with the cell lysate and a Master Mix containing reverse transcription (RT) reagents and poly(dT) RT primers. Incubation of the GEMs produces 10x Barcoded, full-length cDNA from polyadenylated mRNA.
What are UMI and TSO? (Chat4)
In single-cell sequencing, both Unique Molecular Identifiers and Template Switch Oligos (TSOs) play vital roles. Let’s explore what they do and why they are important:
Unique Molecular Identifiers (UMI)
-
Error Reduction: Unique Molecular Identifiers (UMIs) are unique sequences added to each molecule before amplification. They help in distinguishing genuine sequences from PCR duplicates, allowing for accurate quantification and detection of DNA or RNA molecules.
-
Quantification: UMIs allow for the absolute quantification of nucleic acid molecules in a sample, crucial for understanding gene expression levels in single-cell studies.
-
Reducing Amplification Bias: By identifying original molecules, UMIs mitigate PCR amplification biases, leading to more representative sequencing data.
Template Switch Oligos (TSOs)
-
cDNA Synthesis and Amplification: In single-cell RNA sequencing, TSOs are used during the reverse transcription of mRNA to cDNA. They have a unique sequence that attaches to the 3’ end of the cDNA. When the reverse transcriptase enzyme reaches the end of the mRNA template, it switches templates to this oligo, effectively adding a known sequence to the cDNA.
-
Full-Length cDNA: TSOs facilitate the generation of full-length cDNA, especially important for accurately characterizing the transcriptome of a single cell.
-
Tagging for Sequencing: The known sequence added by TSOs serves as a universal priming site for subsequent PCR amplification and sequencing, ensuring that all cDNA molecules are uniformly represented.
Why are They Needed?
-
Accuracy: Both MIs and TSOs improve the accuracy of single-cell sequencing by reducing errors and biases, crucial in studies where detecting low-abundance transcripts or minor genetic variations is essential.
-
Representativeness: They help ensure that the sequencing data is representative of the original cellular content, which is vital for understanding cellular heterogeneity and the function of individual cells within tissues.
-
Enhanced Detection: These elements enhance the detection of rare transcripts and genetic variations, which might otherwise be lost or misinterpreted in the noise of sequencing errors and biases.
-
Quantitative Analysis: They enable quantitative analysis of gene expression, which is crucial for comparing different cells or understanding dynamic processes within cells.
In summary, Molecular Identifiers and Template Switch Oligos are integral to the reliability, fidelity, and comprehensiveness of single-cell sequencing, enabling researchers to delve deeper into the complexities of cellular biology at an individual cell level.
 |
|---|
| 5ʹ Gene Expression (GEX) Library Construction |
Single Cell RNA-Seq Notes
https://karobben.github.io/2021/10/31/Bioinfor/sigcellnote1/