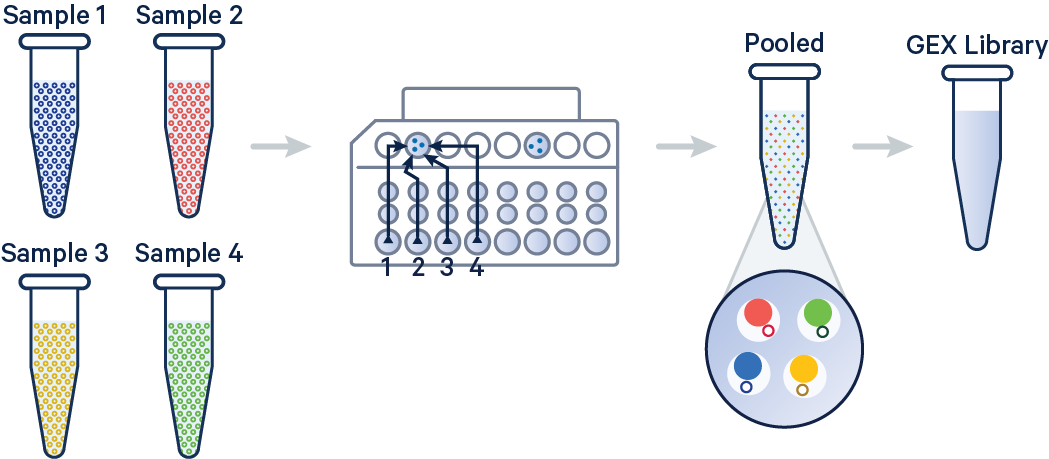
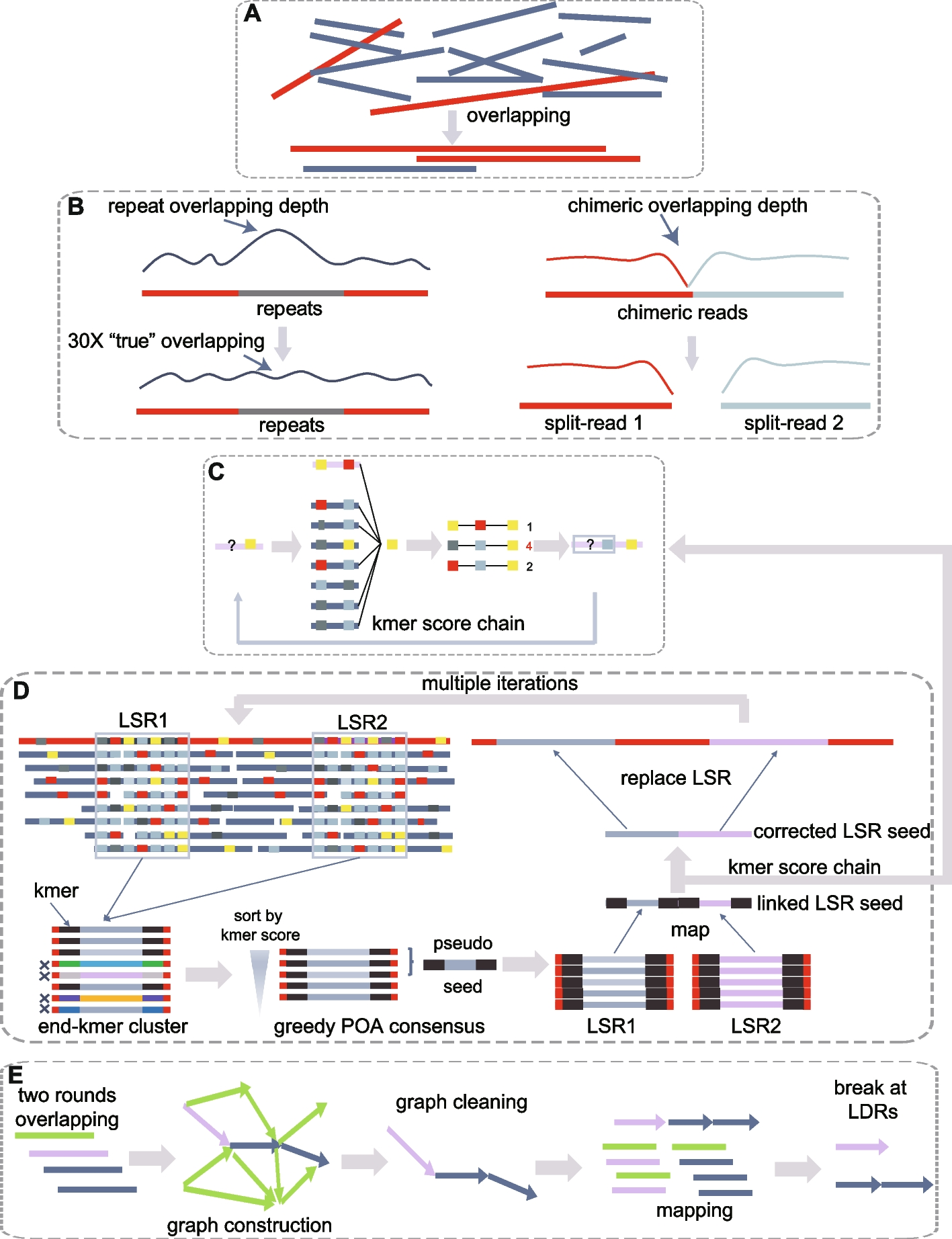
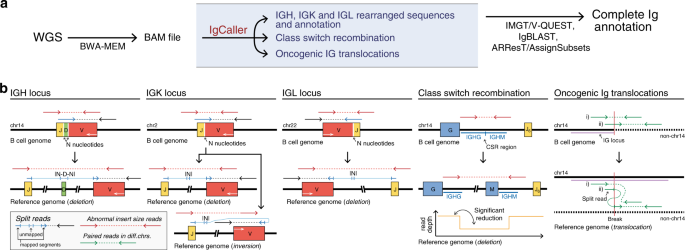
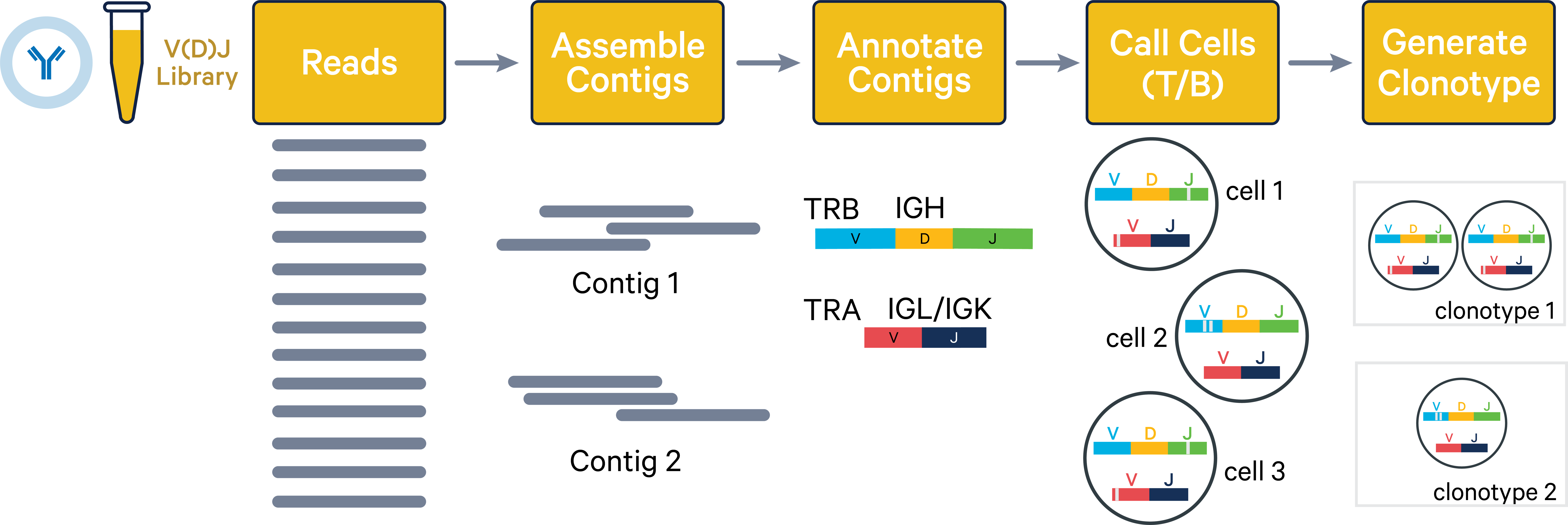
ASCP (Aspera Secure Copy Protocol) is a fast, reliable protocol for transferring large files, particularly over long distances or in conditions with network latency or packet loss. It uses a technology called fasp (Fast, Adaptive, and Secure Protocol) to maximize available bandwidth, making transfers faster than traditional methods like FTP.
For uploading data to NCBI, ASCP is particularly useful because it efficiently handles large datasets, such as genomic sequences or omics data. Its ability to resume interrupted transfers ensures that if a connection fails during an upload, the transfer continues from where it left off, saving time and bandwidth. ASCP also provides strong encryption, ensuring data security during the upload process.
Read more