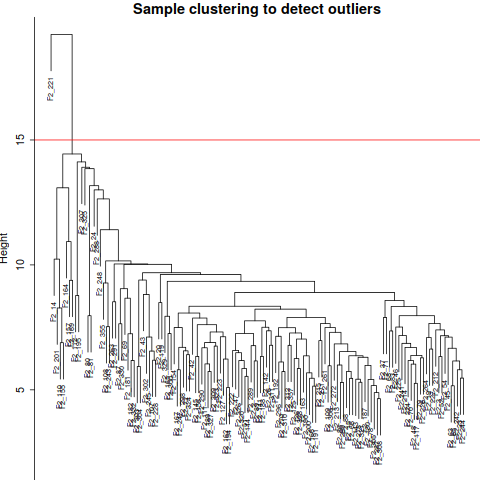
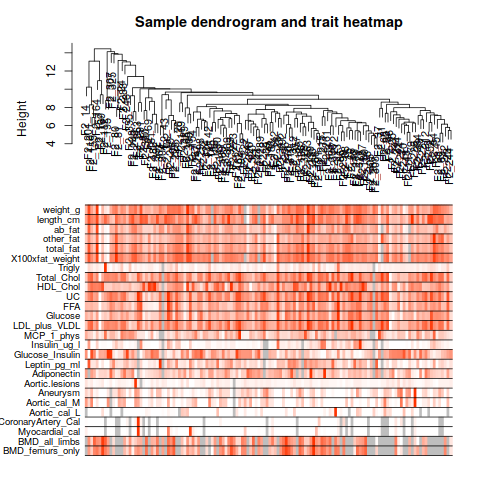
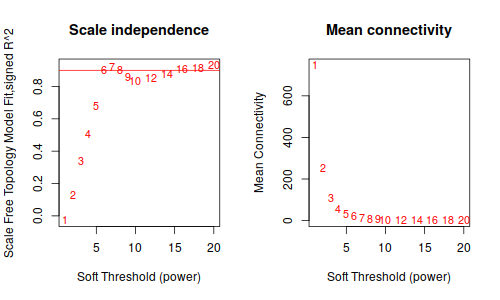
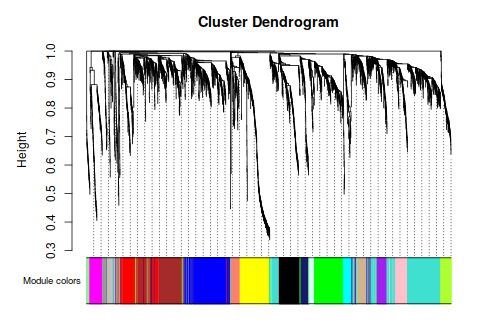
annot = read.csv(file = "GeneAnnotation.csv");
probes = names(datExpr)
probes2annot = match(probes, annot$substanceBXH)
allLLIDs = annot$LocusLinkID[probes2annot];
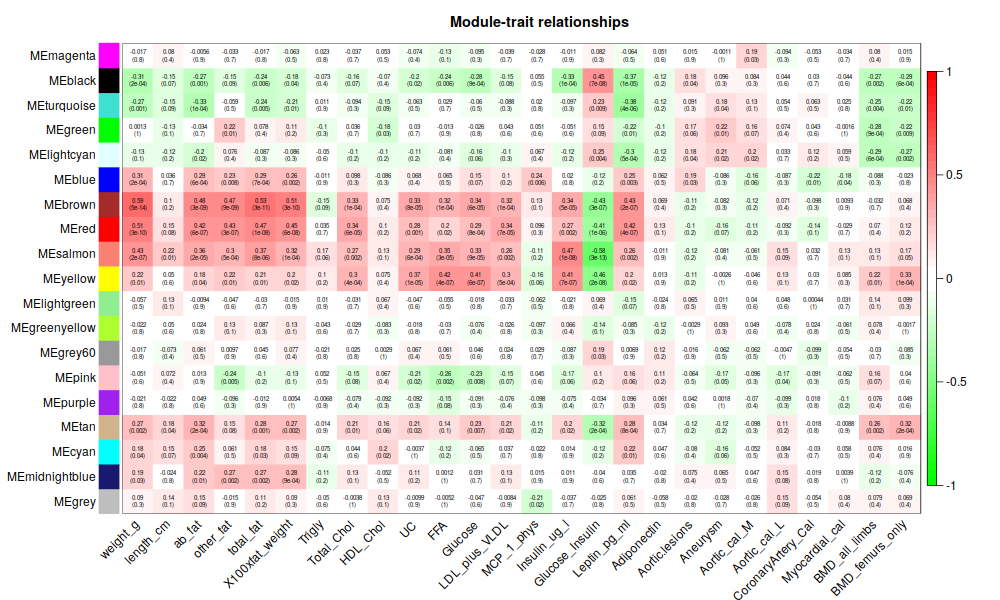
intModules = c("brown", "red", "salmon")
for (module in intModules)
{
modGenes = (moduleColors==module)
modLLIDs = allLLIDs[modGenes];
fileName = paste("LocusLinkIDs-", module, ".txt", sep="");
write.table(as.data.frame(modLLIDs), file = fileName,
row.names = FALSE, col.names = FALSE)
}
fileName = paste("LocusLinkIDs-all.txt", sep="");
write.table(as.data.frame(allLLIDs), file = fileName,
row.names = FALSE, col.names = FALSE)
GOenr = GOenrichmentAnalysis(moduleColors, allLLIDs, organism = "mouse", nBestP = 10);
tab = GOenr$bestPTerms[[4]]$enrichment
write.table(tab, file = "GOEnrichmentTable.csv", sep = ",", quote = TRUE, row.names = FALSE)
keepCols = c(1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 12, 13);
screenTab = tab[, keepCols];
numCols = c(3, 4);
screenTab[, numCols] = signif(apply(screenTab[, numCols], 2, as.numeric), 2)
screenTab[, 7] = substring(screenTab[, 7], 1, 40)
colnames(screenTab) = c("module", "size", "p-val", "Bonf", "nInTerm", "ont", "term name");
rownames(screenTab) = NULL;
options(width=95)
screenTab
|