IMGT®: the international ImMunoGeneTics information system®
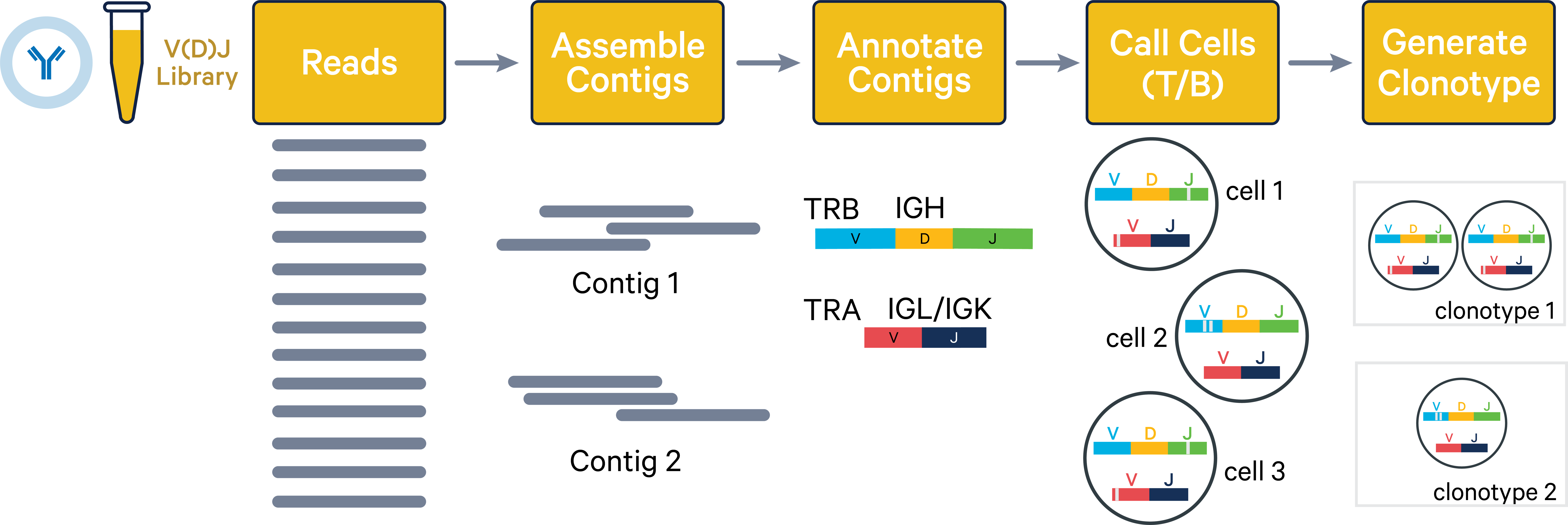
MGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system®, is a comprehensive resource for immunogenetics and immunoinformatics. It was created and has been developed since 1989 by Professor Marie-Paule Lefranc at the Université de Montpellier, France. IMGT® is recognized as the global reference in immunogenetics and immunoinformatics due to its high-quality, integrated knowledge and its standardized nomenclature.
Read more